Dual 19F/1H MR gene reporter molecules for in vivo detection of β-galactosidase
- PMID: 22352428
- PMCID: PMC3320041
- DOI: 10.1021/bc200647q
Dual 19F/1H MR gene reporter molecules for in vivo detection of β-galactosidase
Abstract
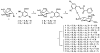
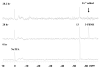
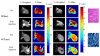
Increased emphasis on personalized medicine and novel therapies requires the development of noninvasive strategies for assessing biochemistry in vivo. The detection of enzyme activity and gene expression in vivo is potentially important for the characterization of diseases and gene therapy. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particularly promising tool, since it is noninvasive and has no associated radioactivity, yet penetrates deep tissue. We now demonstrate a novel class of dual (1)H/(19)F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) lacZ gene reporter molecule to specifically reveal enzyme activity in human tumor xenografts growing in mice. We report the design, synthesis, and characterization of six novel molecules and evaluation of the most effective reporter in mice in vivo. Substrates show a single (19)F NMR signal and exposure to β-galactosidase induces a large (19)F NMR chemical shift response. In the presence of ferric ions, the liberated aglycone generates intense proton MRI T(2) contrast. The dual modality approach allows both the detection of substrate and the imaging of product enhancing the confidence in enzyme detection.
Figures




References
-
- Gilad AA, Winnard PT, van Zijl PCM, Bulte JWM. Developing MR reporter genes: promises and pitfalls. NMR Biomed. 2007;20:275–290. - PubMed
-
- Razgulin A, Ma N, Rao JH. Strategies for in vivo imaging of enzyme activity: an overview and recent advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:4186–4216. - PubMed
-
- Kruger A, Schirrmacher V, Khokha R. The bacterial lacZ gene: An important tool for metastasis research and evaluation of new cancer therapies. Cancer Metast.Rev. 1998;17:285–94. - PubMed
-
- de Almeida RA, Burgess D, Shema R, Motlekar N, Napper AD, Diamond SL, Pavitt GD. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell-based quantitative beta-galactosidase handling and assay compatible with robotic high-throughput screening. Yeast. 2008;25:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Louie AY, Huber MM, Ahrens ET, Rothbacher U, Moats R, Jacobs RE, Fraser SE, Meade TJ. In vivo visualization of gene expression using magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Biotechnol. 2000;18:321–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

