Nitric oxide modulation of low-frequency oscillations in cortical vessels in FHM--a NIRS study
- PMID: 22352839
- PMCID: PMC3730264
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02098.x
Nitric oxide modulation of low-frequency oscillations in cortical vessels in FHM--a NIRS study
Abstract
Background: The pathophysiological alterations in patients with familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM) are not yet fully known. The headache characteristics in patients with FHM mutations have been examined in a series of glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) provocation studies in FHM patients, but the cortical vascular response to GTN in FHM patients has never been investigated before.
Objective: To investigate changes in spontaneous low-frequency oscillations (LFO) of cortical vessels in response to the nitric oxide donor GTN by near-infrared spectroscopy in FHM patients.
Methods: Twenty-three FHM patients without known mutations and 9 healthy controls received a continuous intravenous infusion of GTN 0.5 µg/kg/minute over 20 minutes. Using near-infrared spectroscopy, we recorded oxygenated hemoglobin (oxyHb) LFO amplitude bilateral at the frontal cortex at baseline and 15 minutes and 40 minutes after start of the GTN infusion.
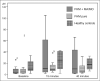
Results: GTN changed oxyHb LFO amplitude in FHM patients (P = .002), but not in healthy controls (P = .121). Only in FHM patients with coexisting common migraine types did GTN infusion induced changes in LFO amplitudes (P < .001), where post-hoc analysis revealed an increase in LFO amplitude 15 minutes (P = .003) and 40 (P = .013) minutes after start of infusion compared with baseline. Interestingly, GTN infusion induced no changes in LFO amplitude in patients with a pure FHM phenotype (P = .695).
Conclusion: FHM patients with a mixed phenotype (coexisting common type of migraine) showed an increase in oxyHb LFO amplitude during GTN infusion, whereas FHM patients with pure phenotype showed no changes. These data suggest possible differences in frontal cortical nitric oxide vascular sensitivity between FHM patients with a mixed phenotype and patients with pure FHM.
© 2012 American Headache Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coexisting typical migraine in familial hemiplegic migraine.Neurology. 2010 Feb 16;74(7):594-600. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cff79d. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 20157162
-
Familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 does not share hypersensitivity to nitric oxide with common types of migraine.Cephalalgia. 2008 Apr;28(4):367-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01542.x. Epub 2008 Feb 22. Cephalalgia. 2008. PMID: 18294248
-
Familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 shows no hypersensitivity to nitric oxide.Cephalalgia. 2008 May;28(5):496-505. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01559.x. Epub 2008 Mar 31. Cephalalgia. 2008. PMID: 18384418 Clinical Trial.
-
Investigations into the role of nitric oxide and the large intracranial arteries in migraine headache.Cephalalgia. 1997 Dec;17(8):873-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1997.1708873.x. Cephalalgia. 1997. PMID: 9453277 Review.
-
Nitric oxide in migraine.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007 Aug;6(4):258-64. doi: 10.2174/187152707781387233. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17691982 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive methods for measuring vascular changes in neurovascular headaches.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Apr;39(4):633-649. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17724138. Epub 2017 Aug 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 28782410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing low-frequency oscillations in cerebrovascular diseases and related conditions with near-infrared spectroscopy: a plausible method for evaluating cerebral autoregulation?Neurophotonics. 2018 Jul;5(3):030901. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.5.3.030901. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Neurophotonics. 2018. PMID: 30689678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IHS The International Classification Of Headache Disorders, 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004;24(Suppl. 1):9–160. - PubMed
-
- Ophoff RA, Terwindt GM, Vergouwe MN, et al. Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell. 1996;87:543–552. - PubMed
-
- Dichgans M, Freilinger T, Eckstein G, et al. Mutation in the neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel SCN1A in familial hemiplegic migraine. Lancet. 2005;366:371–377. - PubMed
-
- De FM, Marconi R, Silvestri L, et al. Haploinsufficiency of ATP1A2 encoding the Na+/K+ pump alpha2 subunit associated with familial hemiplegic migraine type 2. Nat Genet. 2003;33:192–196. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen LL, Kirchmann M, Bjornsson A, et al. The genetic spectrum of a population-based sample of familial hemiplegic migraine. Brain. 2007;130:346–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

