Mechanism of transcription initiation by the yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase
- PMID: 22353467
- PMCID: PMC3381941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.003
Mechanism of transcription initiation by the yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase
Abstract
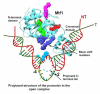
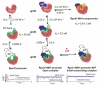
Mitochondria are the major supplier of cellular energy in the form of ATP. Defects in normal ATP production due to dysfunctions in mitochondrial gene expression are responsible for many mitochondrial and aging related disorders. Mitochondria carry their own DNA genome which is transcribed by relatively simple transcriptional machinery consisting of the mitochondrial RNAP (mtRNAP) and one or more transcription factors. The mtRNAPs are remarkably similar in sequence and structure to single-subunit bacteriophage T7 RNAP but they require accessory transcription factors for promoter-specific initiation. Comparison of the mechanisms of T7 RNAP and mtRNAP provides a framework to better understand how mtRNAP and the transcription factors work together to facilitate promoter selection, DNA melting, initiating nucleotide binding, and promoter clearance. This review focuses primarily on the mechanistic characterization of transcription initiation by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae mtRNAP (Rpo41) and its transcription factor (Mtf1) drawing insights from the homologous T7 and the human mitochondrial transcription systems. We discuss regulatory mechanisms of mitochondrial transcription and the idea that the mtRNAP acts as the in vivo ATP "sensor" to regulate gene expression. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Mitochondrial Gene Expression.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

