Advanced morpholino oligomers: a novel approach to antiviral therapy
- PMID: 22353544
- PMCID: PMC7114334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.02.004
Advanced morpholino oligomers: a novel approach to antiviral therapy
Abstract
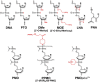
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMOs) are synthetic antisense oligonucleotide analogs that are designed to interfere with translational processes by forming base-pair duplexes with specific RNA sequences. Positively charged PMOs (PMOplus™) are effective for the postexposure protection of two fulminant viral diseases, Ebola and Marburg hemorrhagic fever in nonhuman primates, and this class of antisense agent may also have possibilities for treatment of other viral diseases. PMOs are highly stable, are effective by a variety of routes of administration, can be readily formulated in common isotonic delivery vehicles, and can be rapidly designed and synthesized. These are properties which may make PMOs good candidates for use during responses to emerging or reemerging viruses that may be insensitive to available therapies or for use during outbreaks, especially in regions that lack a modern medical infrastructure. While the efficacy of sequence-specific therapies can be limited by target-site sequence variations that occur between variants or by the emergence of resistant mutants during infections, various PMO design strategies can minimize these impacts. These strategies include the use of promiscuous bases such as inosine to compensate for predicted base-pair mismatches, the use of sequences that target conserved sites between viral strains, and the use of sequences that target host products that viruses utilize for infection.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Amantana A., Iversen P.L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of phosphorodiamidate morpholino antisense oligomers. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5:550–555. - PubMed
-
- Amantana A., Moulton H.M., Cate M.L., Reddy M.T., Whitehead T., Hassinger J.N., Youngblood D.S., Iversen P.L. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, stability and toxicity of a cell-penetrating peptide-morpholino oligomer conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 2007;18:1325–1331. - PubMed
-
- Arora V., Devi G.R., Iversen P.L. Neutrally charged phosphorodiamidate morpholino antisense oligomers: uptake, efficacy and pharmacokinetics. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2004;5:431–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

