Development of square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for determination of acebutolol in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids
- PMID: 22353684
- PMCID: PMC3296636
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-15
Development of square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for determination of acebutolol in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids
Abstract
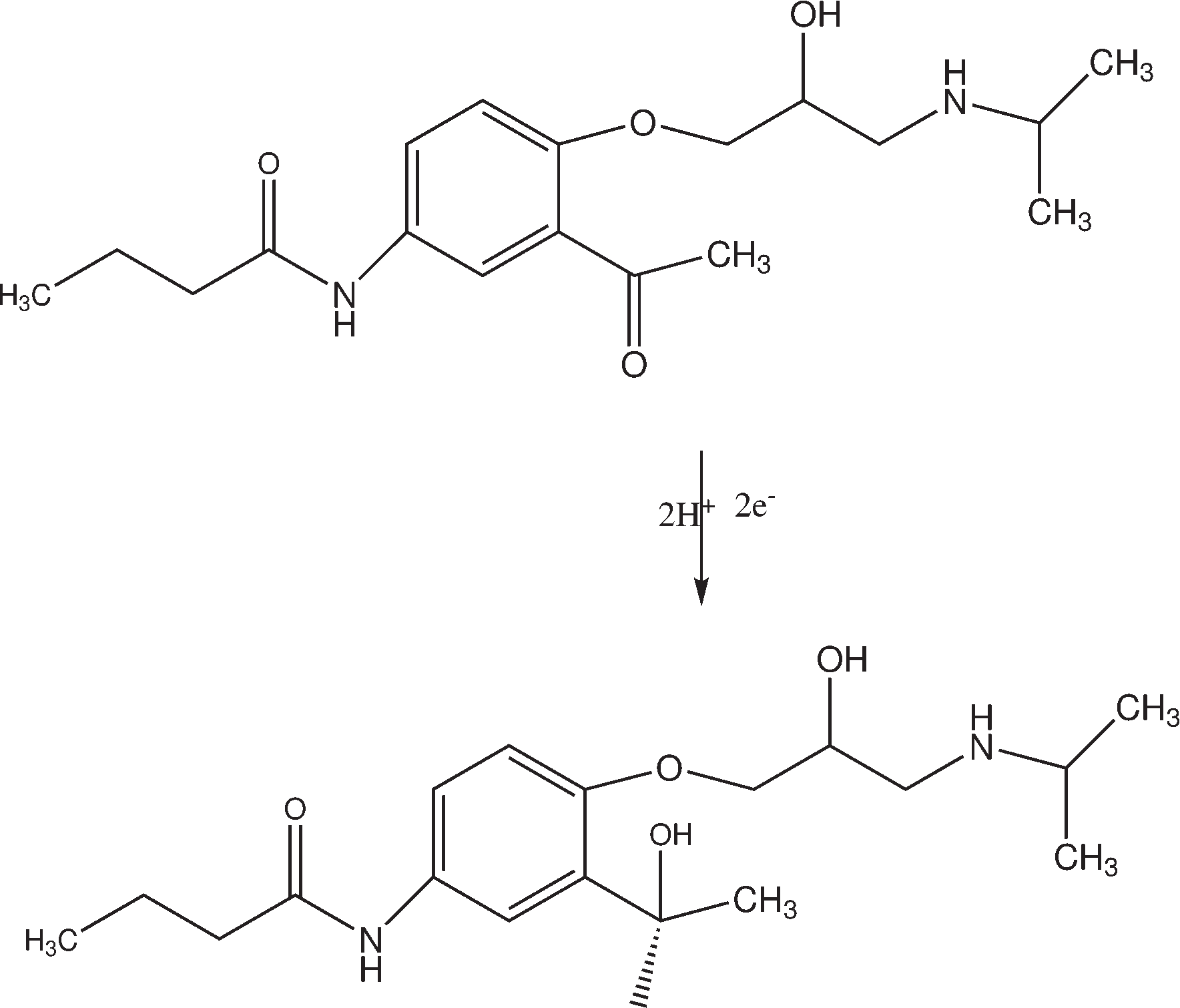
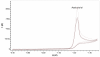
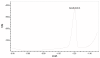
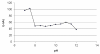
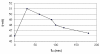
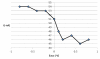
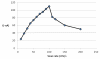
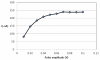
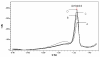
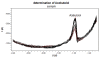
A validated simple, rapid, sensitive and specific square-wave voltammetric technique is described for the determination of acebutolol (AC) following its accumulation onto a hanging mercury drop electrode in a Britton-Robinson universal buffer of pH 7.5. The optimal procedural conditions were: accumulation potential Eacc = - 0.8 V versus Ag/AgCl/KCl, accumulation duration tacc = 30 s, pulse-amplitude = 70 mV, scan rate = 100 mV/s, frequency = 30 Hz, surface area of the working electrode = 0.6 mm2 and the convection rate = 2000 rpm. Under these optimized conditions, the adsorptive stripping voltammetry (AdSV) peak current was proportional over the concentration range 5 × 10-7 - 6 × 10-6 M (r = 0.999). Recoveries for acebutolol from human plasma and urine were in the range 97-103% and 96-104% respectively. The method proved to be precise (intra-day precision expressed as %RSD in human plasma ranged from 2.9 - 3.2% and inter-day precision expressed as %RSD ranged from 3.4 - 3.8%) and accurate (intra-day accuracies expressed as % error in human urine ranged from -3.3 - 2.8% and inter-day accuracies ranged from -3.3 - 1.7%). The limit of quantitation (LOQ) and limit of detection (LOD) for acebutolol were 1.7 × 10-7 and 5 × 10-7 M, respectively. Possible interferences by substances usually present in the pharmaceutical formulations were investigated with a mean recovery of 101.6 ± 0.64%. Results of the developed square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry (SW-AdSV) method were comparable with those obtained by reference analytical method.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A square-wave adsorptive stripping voltammetric method for determination of fast green dye.J AOAC Int. 2009 Nov-Dec;92(6):1714-9. J AOAC Int. 2009. PMID: 20166589
-
Adsorptive stripping anodic voltammetric determination of thioctic Acid in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations.Int J Biomed Sci. 2009 Mar;5(1):54-8. Int J Biomed Sci. 2009. PMID: 23675115 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetric assay of the estrogen drug ethinylestradiol in pharmaceutical formulation and human plasma at a mercury electrode.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006 Feb 13;40(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2005.07.024. Epub 2005 Sep 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006. PMID: 16146680
-
Determination of carmine food dye (E120) in foodstuffs by stripping voltammetry.J AOAC Int. 2009 Sep-Oct;92(5):1454-9. J AOAC Int. 2009. PMID: 19916383
-
Assay of dipyridamole in human serum using cathodic adsorptive square-wave stripping voltammetry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2002 Sep;374(2):289-93. doi: 10.1007/s00216-002-1463-z. Epub 2002 Aug 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2002. PMID: 12324851
Cited by
-
LC and LC-MS/MS studies for the identification and characterization of degradation products of acebutolol.J Pharm Anal. 2018 Dec;8(6):357-365. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 15. J Pharm Anal. 2018. PMID: 30595941 Free PMC article.
-
A high throughput gold nanoparticles chemiluminescence detection of opioid receptor antagonist naloxone hydrochloride.Chem Cent J. 2015 Feb 11;9:6. doi: 10.1186/s13065-015-0083-6. eCollection 2015. Chem Cent J. 2015. PMID: 25705253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parfitt K, editor. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. 33. Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK; 2002.
-
- Delamoye M, Duverneuil C, Paraire F, de Mazancourt P, Alvarez JC. Simultaneous determination of thirteen beta-blockers and one metabolite by gradient high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode-array UV detection. Forensic Sci Int. 2004;141(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2003.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

