Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via an LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis
- PMID: 22353783
- PMCID: PMC3496153
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3128
Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via an LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Honokiol activates AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer cells via LKB1-dependent pathway and inhibits breast carcinogenesis.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 28;19(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0829-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28351375 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Honokiol, a small-molecule polyphenol isolated from magnolia species, is widely known for its therapeutic potential as an antiinflammatory, antithrombosis, and antioxidant agent, and more recently, for its protective function in the pathogenesis of carcinogenesis. In the present study, we sought to examine the effectiveness of honokiol in inhibiting migration and invasion of breast cancer cells and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Methods: Clonogenicity and three-dimensional colony-formation assays were used to examine breast cancer cell growth with honokiol treatment. The effect of honokiol on invasion and migration of breast cancer cells was evaluated by using Matrigel invasion, scratch-migration, spheroid-migration, and electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS)-based migration assays. Western blot and immunofluorescence analysis were used to examine activation of the liver kinase B1 (LKB1)-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) axis. Isogenic LKB1-knockdown breast cancer cell line pairs were developed. Functional importance of AMPK activation and LKB1 overexpression in the biologic effects of honokiol was examined by using AMPK-null and AMPK-wild type (WT) immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and isogenic LKB1-knockdown cell line pairs. Finally, mouse xenografts, immunohistochemical and Western blot analysis of tumors were used.
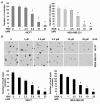
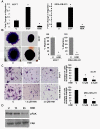
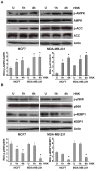
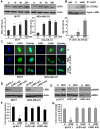
Results: Analysis of the underlying molecular mechanisms revealed that honokiol treatment increases AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and activity, as evidenced by increased phosphorylation of the downstream target of AMPK, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC) and inhibition of phosphorylation of p70S6kinase (pS6K) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (4EBP1). By using AMPK-null and AMPK-WT (MEFs), we found that AMPK is required for honokiol-mediated modulation of pACC-pS6K. Intriguingly, we discovered that honokiol treatment increased the expression and cytoplasmic translocation of tumor-suppressor LKB1 in breast cancer cells. LKB1 knockdown inhibited honokiol-mediated activation of AMPK and, more important, inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, honokiol treatment resulted in inhibition of breast tumorigenesis in vivo. Analysis of tumors showed significant increases in the levels of cytoplasmic LKB1 and phospho-AMPK in honokiol-treated tumors.
Conclusions: Taken together, these data provide the first in vitro and in vivo evidence of the integral role of the LKB1-AMPK axis in honokiol-mediated inhibition of the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. In conclusion, honokiol treatment could potentially be a rational therapeutic strategy for breast carcinoma.
Figures


References
-
- Fujita M, Itokawa H, Sashida Y. [Studies on the components of Magnolia obovata Thunb. 3. Occurrence of magnolol and honokiol in M. obovata and other allied plants] Yakugaku Zasshi. 1973;93:429–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

