MicroRNA-101 (miR-101) post-transcriptionally regulates the expression of EP4 receptor in colon cancers
- PMID: 22353936
- PMCID: PMC3336073
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.13.3.18874
MicroRNA-101 (miR-101) post-transcriptionally regulates the expression of EP4 receptor in colon cancers
Abstract
Purpose: Expression of the PGE2 receptor, EP4, is up-regulated during colorectal carcinogenesis. However the mechanism leading to deregulation of the EP4 receptor is not known. The present study was conducted to investigate the regulation of EP4 receptor by miRNAs.
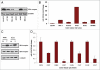
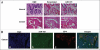
Experimental design: We analyzed 26 colon cancers (i.e. 15 adenocarcinomas and 9 adenomas) and 16 normal colon specimens for EP4 receptor expression by immunohistochemistry. A bioinformatics approached identified putative microRNA binding sites with the 3'-UTR of the EP4 receptor. Both colon cancer cell lines and tumor specimens were analyzed for miR-101 and EP4 expression by qRT-PCR and Western analysis respectively and simultaneously in situ hybridizations was used to confirm our results. In vitro and in vivo assays were used to confirm our clinical findings.
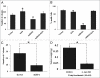
Results: We observed an inverse correlation between the levels of miR-101 and EP4 receptor protein. Transfection of LS174T cells with miR-101 significantly suppressed a luciferase reporter containing the EP4 receptor-3'-UTR. In contrast, a mutant EP4 receptor-3'-UTR construct was unaffected. Ectopic expression of miR-101 markedly reduced cell proliferation and motility. Co-transfection of EP4 receptor could rescue colon cancer cells from the tumor suppressive effects of miR-101. Moreover, the pharmacologic inhibition of EP4 receptor signaling or silencing of EP4 receptor phenocopied the effect of miR-101. This is the first study to show that the EP4 receptor is negatively regulated by miR-101.
Conclusions: These data provide new insights in the modulation of EP-4 receptor expression at the post-transcriptional level by miR-101 and suggests therapeutic strategies against miR-101 targets may be warranted.
Figures



References
-
- Rothenberg ML, Oza AM, Bigelow RH, Berlin JD, Marshall JL, Ramanathan RK, et al. Superiority of oxaliplatin and fluorouracil-leucovorin compared with either therapy alone in patients with progressive colorectal cancer after irinotecan and fluorouracilleucovorin: interim results of a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2059–2069. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.11.126. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rougier P, Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E, Niderele N, Possinger K, Labianca R, et al. Randomised trial of irinotecan versus fluorouracil by continuous infusion after fluorouracil failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1998;352:1407–1412. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)03085-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rougier P, Paillot B, LaPlanche A, Morvan F, Seitz JF, Rekacewicz C, et al. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) continuous intravenous infusion compared with bolus administration. Final results of a randomised trial in metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 1997;33:1789–1793. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(97)00175-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
