Tumor-targeted T cells modified to secrete IL-12 eradicate systemic tumors without need for prior conditioning
- PMID: 22354001
- PMCID: PMC3359735
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-400044
Tumor-targeted T cells modified to secrete IL-12 eradicate systemic tumors without need for prior conditioning
Abstract
Adoptive cell therapy with tumor-targeted T cells is a promising approach to cancer therapy. Enhanced clinical outcome using this approach requires conditioning regimens with total body irradiation, lymphodepleting chemotherapy, and/or additional cytokine support. However, the need for prior conditioning precludes optimal application of this approach to a significant number of cancer patients intolerant to these regimens. Herein, we present preclinical studies demonstrating that treatment with CD19-specific, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T cells that are further modified to constitutively secrete IL-12 are able to safely eradicate established disease in the absence of prior conditioning. We demonstrate in a novel syngeneic tumor model that tumor elimination requires both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell subsets, autocrine IL-12 stimulation, and subsequent IFNγ secretion by the CAR(+) T cells. Importantly, IL-12-secreting, tumor-targeted T cells acquire intrinsic resistance to T regulatory cell-mediated inhibition. Based on these preclinical data, we anticipate that adoptive therapy using CAR-targeted T cells modified to secrete IL-12 will obviate or reduce the need for potentially hazardous conditioning regimens to achieve optimal antitumor responses in cancer patients.
Figures
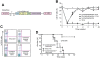
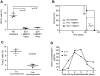




Comment in
-
The power and pitfalls of IL-12.Blood. 2012 May 3;119(18):4096-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-415018. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22555659
References
-
- Brentjens RJ, Latouche JB, Santos E, et al. Eradication of systemic B-cell tumors by genetically targeted human T lymphocytes co-stimulated by CD80 and interleukin-15. Nat Med. 2003;9(3):279–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 CA095152/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138738/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA95152/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI56363/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI056363/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA059350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA08748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA059350/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057157/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA138738/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

