In vitro antibacterial and time-kill assessment of crude methanolic stem bark extract of Acacia mearnsii de wild against bacteria in shigellosis
- PMID: 22354188
- PMCID: PMC6268967
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17022103
In vitro antibacterial and time-kill assessment of crude methanolic stem bark extract of Acacia mearnsii de wild against bacteria in shigellosis
Abstract
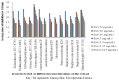
Shigellosis is an important cause of worldwide morbidity and mortality among young children and old people for which treatment with antimicrobial agents is limited. Hence, the need for curative potentials obtainable from medicinal plants becomes inevitable. This study was carried out to assess the antibacterial potentials of crude methanolic extract of the stem bark of Acacia mearnsii against some selected bacteria of clinical importance in shigellosis. The bacteria were inhibited by the extract to produce concentration dependent inhibition zones. The extract exhibited a varied degree of antibacterial activity against all the tested isolates. The MIC values for Gram negative (0.0391-0.3125) mg/mL and those of Gram positive bacteria (0.0781-0.625) mg/mL indicated that the Gram negative bacteria were more inhibited by the extract than the Gram positive bacteria. Average log reduction in viable cell count in time-kill assay ranged between -2.456 Log₁₀ to 2.230 Log₁₀ cfu/mL after 4 h of interaction, and between -2.921 Log₁₀ and 1.447 Log₁₀ cfu/mL after 8 h interaction in 1× MIC and 2× MIC of the extract. The study provided scientific justification for the use of the crude methanolic extract from the stem bark of A. mearnsii in shigellosis. The degree of the antibacterial activity indicated that the crude extract is a potential source of bioactive compounds that could be useful for the development of new antimicrobial agents capable of decreasing the burden of drug resistance and cost of management of diseases of clinical and public health importance in South Africa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic interactions of methanolic extract of Acacia mearnsii De Wild. with antibiotics against bacteria of clinical relevance.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(7):8915-8932. doi: 10.3390/ijms13078915. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22942742 Free PMC article.
-
Tannins from Acacia mearnsii De Wild. Bark: Tannin Determination and Biological Activities.Molecules. 2018 Apr 5;23(4):837. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040837. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29621196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of antibiotics and methanolic crude extracts of Afzelia Africana (Smith.) against drug resistance bacterial isolates.Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(7):4477-503. doi: 10.3390/ijms12074477. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Int J Mol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21845091 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial, Antibiofilm, and Efflux Pump Inhibitory Properties of the Crude Extract and Fractions from Acacia macrostachya Stem Bark.ScientificWorldJournal. 2021 Oct 21;2021:5381993. doi: 10.1155/2021/5381993. eCollection 2021. ScientificWorldJournal. 2021. PMID: 34720766 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteria, stem cells and cancer.Cancer Gene Ther. 2025 Mar;32(3):269-272. doi: 10.1038/s41417-025-00876-x. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Cancer Gene Ther. 2025. PMID: 39915606 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Novel Pleuromutilin Derivatives as Potent Antibacterial Agents for the Treatment of MRSA Infection.Molecules. 2022 Jan 29;27(3):931. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030931. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164203 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-Class Cyclic Temporin L Analogue: Design, Synthesis, and Antimicrobial Assessment.J Med Chem. 2021 Aug 12;64(15):11675-11694. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01033. Epub 2021 Jul 23. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34296619 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Synergy-Based Combination of Methanolic Extract of Andrographis paniculata and Berberis aristata Against E. coli and S. aureus.Curr Microbiol. 2022 Jun 15;79(8):223. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02911-8. Curr Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35704102
-
Anti-Shigellosis Activity of Cola anomala Water/Ethanol Pods Extract on Shigella flexneri-Induced Diarrhea in Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Nov 11;2019:6706230. doi: 10.1155/2019/6706230. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31828116 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the antibacterial activity of Khaya senegalensis [(Desr.) A. Juss)] stem bark extract on Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi [(ex Kauffmann and Edwards) Le Minor and Popoff].Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014 May;4(Suppl 1):S279-83. doi: 10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C636. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014. PMID: 25183098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastos F.C., Loureiro E.C. Antimicrobial Resistance of Shigella spp. isolated in the State of Pará, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011;44:607–610. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S., Mishra B., Muralidharan S., Srinivasa H. Ceftriaxone resistant Shigella flexneri, an emerging problem. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2010;64:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Huang I.F., Chiu C.H., Wang M.H., Wu C.Y., Hsieh K.S., Chiou C.C. Outbreak of dysentery associated with Ceftriaxone-resistant Shigella sonnei: First report of Plasmid-Mediated CMY-2-Type AmpC ß-Lactamase resistance in S. sonnei. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005;43:2608–2612. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2608-2612.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay U.K., Gupta S., Dutta S. Search for shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC) including 0157: H7 strains in and around Kolkata. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2003;21:17–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases