Target- and resistance-based mechanistic studies with TP-434, a novel fluorocycline antibiotic
- PMID: 22354310
- PMCID: PMC3346605
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.06187-11
Target- and resistance-based mechanistic studies with TP-434, a novel fluorocycline antibiotic
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Grossman et al., target- and resistance-based mechanistic studies with TP-434, a novel fluorocycline antibiotic.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Sep;59(9):5870. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01551-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26276898 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
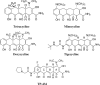
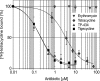
TP-434 is a novel, broad-spectrum fluorocycline antibiotic with activity against bacteria expressing major antibiotic resistance mechanisms, including tetracycline-specific efflux and ribosomal protection. The mechanism of action of TP-434 was assessed using both cell-based and in vitro assays. In Escherichia coli cells expressing recombinant tetracycline resistance genes, the MIC of TP-434 (0.063 μg/ml) was unaffected by tet(M), tet(K), and tet(B) and increased to 0.25 and 4 μg/ml in the presence of tet(A) and tet(X), respectively. Tetracycline, in contrast, was significantly less potent (MIC ≥ 128 μg/ml) against E. coli cells when any of these resistance mechanisms were present. TP-434 showed potent inhibition in E. coli in vitro transcription/translation (50% inhibitory concentration [IC(50)] = 0.29 ± 0.09 μg/ml) and [(3)H]tetracycline ribosome-binding competition (IC(50) = 0.22 ± 0.07 μM) assays. The antibacterial potencies of TP-434 and all other tetracycline class antibiotics tested were reduced by 4- to 16-fold, compared to that of the wild-type control strain, against Propionibacterium acnes strains carrying a 16S rRNA mutation, G1058C, a modification that changes the conformation of the primary binding site of tetracycline in the ribosome. Taken together, the findings support the idea that TP-434, like other tetracyclines, binds the ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis and that this activity is largely unaffected by the common tetracycline resistance mechanisms.
Figures
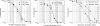
References
-
- Bauer G, Berens C, Projan SJ, Hillen W. 2004. Comparison of tetracycline and tigecycline binding sites to ribosomes mapped by dimethylsulphate and drug-directed Fe2+ cleavage of 16S rRNA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53:592–599 - PubMed
-
- Brodersen DE, et al. 2000. The structural basis for the action of the antibiotics tetracycline, pactamycin and hygromycin B on the 30S ribosomal subunit. Cell 103:1143–1154 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

