RIPPLY3 is a retinoic acid-inducible repressor required for setting the borders of the pre-placodal ectoderm
- PMID: 22354841
- PMCID: PMC3283127
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.071456
RIPPLY3 is a retinoic acid-inducible repressor required for setting the borders of the pre-placodal ectoderm
Abstract
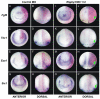
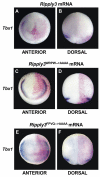
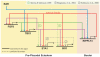
Retinoic acid signaling is a major component of the neural posteriorizing process in vertebrate development. Here, we identify a new role for the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) in the anterior of the embryo, where RAR regulates Fgf8 expression and formation of the pre-placodal ectoderm (PPE). RARα2 signaling induces key pre-placodal genes and establishes the posterolateral borders of the PPE. RAR signaling upregulates two important genes, Tbx1 and Ripply3, during early PPE development. In the absence of RIPPLY3, TBX1 is required for the expression of Fgf8 and hence, PPE formation. In the presence of RIPPLY3, TBX1 acts as a transcriptional repressor, and functions to restrict the positional expression of Fgf8, a key regulator of PPE gene expression. These results establish a novel role for RAR as a regulator of spatial patterning of the PPE through Tbx1 and RIPPLY3. Moreover, we demonstrate that Ripply3, acting downstream of RAR signaling, is a key player in establishing boundaries in the PPE.
Figures
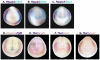
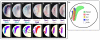
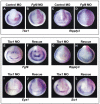
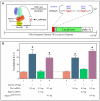
Similar articles
-
Multiple points of interaction between retinoic acid and FGF signaling during embryonic axis formation.Development. 2004 Jun;131(11):2653-67. doi: 10.1242/dev.01129. Epub 2004 May 5. Development. 2004. PMID: 15128657
-
Tissues and signals involved in the induction of placodal Six1 expression in Xenopus laevis.Dev Biol. 2005 Dec 1;288(1):40-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.07.022. Epub 2005 Nov 4. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16271713
-
Fam46a regulates BMP-dependent pre-placodal ectoderm differentiation in Xenopus.Development. 2018 Oct 26;145(20):dev166710. doi: 10.1242/dev.166710. Development. 2018. PMID: 30291163
-
Retinoic acid regulation of the somitogenesis clock.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2007 Jun;81(2):84-92. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20092. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2007. PMID: 17600781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feedback Regulation of Signaling Pathways for Precise Pre-Placodal Ectoderm Formation in Vertebrate Embryos.J Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 26;10(3):35. doi: 10.3390/jdb10030035. J Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36135368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac stem cells: Current knowledge and future prospects.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Jan 26;14(1):1-40. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i1.1. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35126826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the pre-placodal transcriptome to reveal presumptive direct targets of Six1 and Eya1 in cranial placodes.Elife. 2016 Aug 31;5:e17666. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17666. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27576864 Free PMC article.
-
Tbx1 represses Mef2c gene expression and is correlated with histone 3 deacetylation of the anterior heart field enhancer.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Aug 30;11(9):dmm029967. doi: 10.1242/dmm.029967. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 30166330 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of cranial sensory placode development.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;111:301-50. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.009. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25662264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A loss-of-function mutation p.T52S in RIPPLY3 is a potential predisposing genetic risk factor for Chinese Han conotruncal heart defect patients without the 22q11.2 deletion/duplication.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 21;16(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1633-1. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30241482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahrens K., Schlosser G. (2005). Tissues and signals involved in the induction of placodal Six1 expression in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 288, 40–59 - PubMed
-
- Arima K., Shiotsugu J., Niu R., Khandpur R., Martinez M., Shin Y., Koide T., Cho K. W., Kitayama A., Ueno N., et al. (2005). Global analysis of RAR-responsive genes in the Xenopus neurula using cDNA microarrays. Dev. Dyn. 232, 414–431 - PubMed
-
- Ataliotis P., Ivins S., Mohun T. J., Scambler P. J. (2005). XTbx1 is a transcriptional activator involved in head and pharyngeal arch development in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Dyn. 232, 979–991 - PubMed
-
- Balkany T. J., Downs M. P., Jafek B. W., Krajicek M. J. (1979). Hearing loss in Down’s syndrome. A treatable handicap more common than generally recognized. Clin. Pediatr. 18, 116–118 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

