De-SUMOylation of CCCTC binding factor (CTCF) in hypoxic stress-induced human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 22354964
- PMCID: PMC3320996
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286641
De-SUMOylation of CCCTC binding factor (CTCF) in hypoxic stress-induced human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
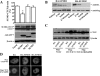
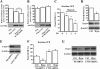
Epigenetic factor CCCTC binding factor (CTCF) plays important roles in the genetic control of cell fate. Previous studies found that CTCF is positively and negatively regulated at the transcriptional level by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and ultraviolet (UV) stimulation, respectively. However, it is unknown whether other stresses modify the CTCF protein. Here, we report that regulation of CTCF by de-SUMOylation is dependent upon hypoxic and oxidative stresses. We found that stimulation of human corneal epithelial cells with hypoxic stress suppressed a high molecular mass form of CTCF (150 kDa), but not a lower molecular weight form of CTCF (130 kDa). Further investigation revealed that the hypoxic stress-suppressed 150-kDa CTCF was a small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)ylated form of the protein. Hypoxic stress-induced de-SUMOylation of human CTCF was associated with lysine 74 and 689 residues, but not to the phosphorylation of CTCF. Overexpression of SENP1 induced de-SUMOylation of CTCF. However, knockdown of SENP1 could not rescue hypoxic stress-induced CTCF de-SUMOylation. Overexpression of SUMO1 and SUMO2 increased SUMOylation of CTCF and partially blocked hypoxic stress-induced CTCF de-SUMOylation, suggesting that free cellular SUMO proteins play roles in regulating hypoxia-induced CTCF de-SUMOylation. In addition, hypoxic stress significantly inhibited PAX6 mRNA and protein expressions by suppression of PAX6-P0 promoter activity. The result was further supported by data showing that knockdown of CTCF significantly enhanced expression of PAX6 and abolished hypoxia-induced suppression of PAX6. Thus, we conclude that hypoxic stress induces de-SUMOylation of CTCF to functionally regulate CTCF activity.
Figures



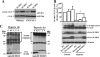
References
-
- Lu L., Reinach P. S., Kao W. W. (2001) Exp. Biol. Med. 226, 653–664 - PubMed
-
- Kimura K., Teranishi S., Kawamoto K., Nishida T. (2010) Exp. Eye Res. 90, 337–343 - PubMed
-
- Teranishi S., Kimura K., Kawamoto K., Nishida T. (2008) Protection of human corneal epithelial cells from hypoxia-induced disruption of barrier function by keratinocyte growth factor. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 49, 2432–2437 - PubMed
-
- Yanai R., Liu Y., Ko J. A., Nishida T. (2008) Effects of ambient oxygen concentration on the proliferation and viability of cultured human corneal epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 86, 412–418 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

