p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis in p53 protein-deficient cells is mediated by BH3-only protein-independent derepression of Bak protein through down-regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL proteins
- PMID: 22354970
- PMCID: PMC3366797
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.314898
p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis in p53 protein-deficient cells is mediated by BH3-only protein-independent derepression of Bak protein through down-regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL proteins
Abstract
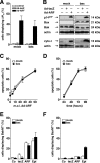
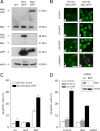
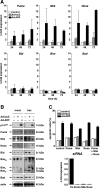
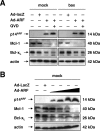
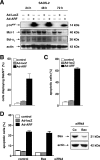
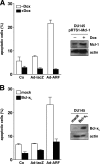
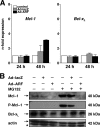
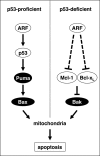
The p14(ARF) tumor suppressor plays a central role in regulating cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. We reported previously that p14(ARF) is capable of triggering apoptosis in a p53-independent manner. However, the mechanism remained unclear. Here we demonstrate that the p53-independent activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway by p14(ARF) is primarily mediated by the pro-apoptotic Bax-homolog Bak. Expression of p14(ARF) exclusively triggers a N-terminal conformational switch of Bak, but not Bax, which allows for mitochondrial permeability shift, release of cytochrome c, activation of caspases, and subsequent fragmentation of genomic DNA. Although forced expression of Bak markedly sensitizes toward p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis, re-expression of Bax has no effect. Vice versa, knockdown of Bak by RNA interference attenuates p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis, whereas down-regulation of Bax has no effect. Bak activation coincides with a prominent, caspase-independent deprivation of the endogenous Bak inhibitors Mcl-1 and Bcl-x(L). In turn, mitochondrial apoptosis is fully blocked by overexpression of either Mcl-1 or Bcl-x(L). Taken together, these data indicate that in the absence of functional p53 and Bax, p14(ARF) triggers mitochondrial apoptosis signaling by activating Bak, which is facilitated by down-regulating anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 and Bcl-x(L). Moreover, our data suggest that the simultaneous inhibition of two central endogenous Bak inhibitors, i.e. Mcl-1 and Bcl-x(L), may be sufficient to activate mitochondrial apoptosis in the absence of BH3-only protein regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Mao L., Merlo A., Bedi G., Shapiro G. I., Edwards C. D., Rollins B. J., Sidransky D. (1995) A novel p16INK4A transcript. Cancer Res. 55, 2995–2997 - PubMed
-
- Duro D., Bernard O., Della Valle V., Berger R., Larsen C. J. (1995) A new type of p16INK4/MTS1 gene transcript expressed in B-cell malignancies. Oncogene 11, 21–29 - PubMed
-
- Quelle D. E., Zindy F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. (1995) Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell 83, 993–1000 - PubMed
-
- Stone S., Jiang P., Dayananth P., Tavtigian S. V., Katcher H., Parry D., Peters G., Kamb A. (1995) Complex structure and regulation of the P16 (MTS1) locus. Cancer Res. 55, 2988–2994 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

