Determinants for activation of the atypical AGC kinase Greatwall during M phase entry
- PMID: 22354989
- PMCID: PMC3318580
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06525-11
Determinants for activation of the atypical AGC kinase Greatwall during M phase entry
Abstract
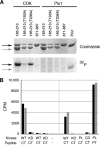
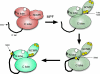
The atypical AGC kinase Greatwall (Gwl) mediates a pathway that prevents the precocious removal of phosphorylations added to target proteins by M phase-promoting factor (MPF); Gwl is thus essential for M phase entry and maintenance. Gwl itself is activated by M phase-specific phosphorylations that are investigated here. Many phosphorylations are nonessential, being located within a long nonconserved region, any part of which can be deleted without effect. Using mass spectrometry and mutagenesis, we have identified 3 phosphorylation sites (phosphosites) critical to Gwl activation (pT193, pT206, and pS883 in Xenopus laevis) located in evolutionarily conserved domains that differentiate Gwl from related kinases. We propose a model in which the initiating event for Gwl activation is phosphorylation by MPF of the proline-directed sites T193 and T206 in the presumptive activation loop. After this priming step, Gwl can intramolecularly phosphorylate its C-terminal tail at pS883; this site probably plays a role similar to that of the tail/Z motif of other AGC kinases. These events largely (but not completely) explain the full activation of Gwl at M phase.
Figures
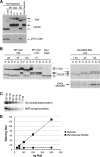
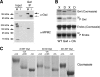

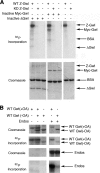



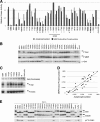




Comment in
-
Stable government of mitosis by Greatwall: the emperor's best servant.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;32(8):1334-6. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00213-12. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22393256 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adams JA. 2003. Activation loop phosphorylation and catalysis in protein kinases: is there functional evidence for the autoinhibitor model? Biochemistry 42: 601–607 - PubMed
-
- Behn-Krappa A, Newton AC. 1999. The hydrophobic phosphorylation motif of conventional protein kinase C is regulated by autophosphorylation. Curr. Biol. 9: 728–737 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
