Alternative splicing within the elk-1 5' untranslated region serves to modulate initiation events downstream of the highly conserved upstream open reading frame 2
- PMID: 22354998
- PMCID: PMC3347237
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06751-11
Alternative splicing within the elk-1 5' untranslated region serves to modulate initiation events downstream of the highly conserved upstream open reading frame 2
Abstract
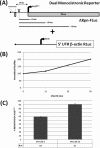
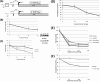
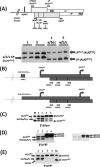
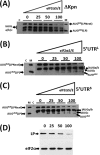
The 5' untranslated region (UTR) plays a central role in the regulation of mammalian translation initiation. Key components include RNA structure, upstream AUGs (uAUGs), upstream open reading frames (uORFs), and internal ribosome entry site elements that can interact to modulate the readout. We previously reported the characterization of two alternatively spliced 5' UTR isoforms of the human elk-1 gene. Both contain two uAUGs and a stable RNA stem-loop, but the long form (5' UTR(L)) was more repressive than the short form (5' UTR(S)) for initiation at the ELK-1 AUG. We now demonstrate that ELK-1 expression arises by a combination of leaky scanning and reinitiation, with the latter mediated by the small uORF2 conserved in both spliced isoforms. In HEK293T cells, a considerable fraction of ribosomes scans beyond the ELK-1 AUG in a reinitiation mode. These are sequestered by a series of out-of-frame AUG codons that serve to prevent access to a second in-frame AUG start site used to express short ELK-1 (sELK-1), an N-terminally truncated form of ELK-1 that has been observed only in neuronal cells. We present evidence that all these events are fine-tuned by the nature of the 5' UTR and the activity of the α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and provide insights into the neuronal specificity of sELK-1 expression.
Figures


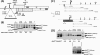
Similar articles
-
Alternatively spliced isoforms of the human elk-1 mRNA within the 5' UTR: implications for ELK-1 expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(14):4649-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm482. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17591614 Free PMC article.
-
5'-untranslated regions with multiple upstream AUG codons can support low-level translation via leaky scanning and reinitiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 27;32(4):1382-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh305. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14990743 Free PMC article.
-
Control of eukaryotic protein synthesis by upstream open reading frames in the 5'-untranslated region of an mRNA.Biochem J. 2002 Oct 1;367(Pt 1):1-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011706. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12117416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative and translation termination-dependent positive control of FLI-1 protein synthesis by conserved overlapping 5' upstream open reading frames in Fli-1 mRNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(9):2959-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.9.2959-2969.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10757781 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of plant translation by upstream open reading frames.Plant Sci. 2014 Jan;214:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24268158 Review.
Cited by
-
An AUG codon conserved for protein function rather than translational initiation: the story of the protein sElk1.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 18;9(7):e102890. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102890. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25036748 Free PMC article.
-
Functional transcriptomics in the post-ENCODE era.Genome Res. 2013 Dec;23(12):1961-73. doi: 10.1101/gr.161315.113. Epub 2013 Oct 30. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 24172201 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding sORF translation - from small proteins to gene regulation.RNA Biol. 2016 Nov;13(11):1051-1059. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1218589. Epub 2016 Aug 12. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27653973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of heterogeneous Transcription Start Sites (TSS) on the translatome: implications for the mammalian cellular phenotype.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 21;16:986. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2179-8. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26589636 Free PMC article.
-
What Is the Impact of mRNA 5' TL Heterogeneity on Translational Start Site Selection and the Mammalian Cellular Phenotype?Front Genet. 2016 Aug 31;7:156. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00156. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27630668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
