RNA-seq analysis of the functional compartments within the rat placentation site
- PMID: 22355068
- PMCID: PMC5393303
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-1833
RNA-seq analysis of the functional compartments within the rat placentation site
Abstract
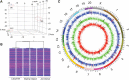
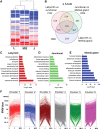
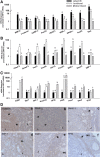
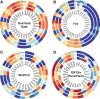
The rat placentation site is distinctly organized into interacting zones, the so-called labyrinth, junctional, and metrial gland compartments. These zones house unique cell populations equipped to undertake myriad prescribed functions including transport, hormonal responses, and immune interactions. Although much is known about the genesis of these cell types and specific markers that characterize each zone, a detailed global overview of gene expression in the three zones is absent. In this report, we used massively parallel sequencing (RNA-seq) to assess mRNA expression profiles and generated transcriptomic maps for each zone of the late-gestation rat placentation site (18.5 d postcoitum). Analysis of expression profiles revealed that each compartment expressed a unique signature, characterized by biological processes specific to the zone. Transport and vasculature-related processes predominated in the labyrinth, hormone secretion in the junctional, and immune interactions in the metrial gland. Furthermore, our analysis identified approximately 4000 differentially expressed genes within the zones. Using k-means clustering, we identified transcription factors with highest expression in either labyrinth, junctional, or metrial gland. Direct interaction (pathway) analysis revealed unique transcription factor networks operating in each compartment. The site-specific expression of 27 transcription factors in the three zones was ascertained via quantitative PCR and protein expression of six transcription factors was confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Finally, we elucidated the expression of key developmentally important families (Sox, GATA, Fox, Wnt, Tead, and IGF/IGFBP) in the placentation site to reveal novel expression of these several factors. The present dataset provides a novel resource to understand zonal gene expression and function in the placenta.
Figures

References
-
- Cross JC. 2006. Placental function in development and disease. Reprod Fertil Dev 18:71–76 - PubMed
-
- Hu D , Cross JC. 2010. Development and function of trophoblast giant cells in the rodent placenta. Int J Dev Biol 54:341–354 - PubMed
-
- Rossant J , Cross JC. 2001. Placental development: lessons from mouse mutants. Nat Rev Genet 2:538–548 - PubMed
-
- Ain R , Canham LN , Soares MJ. 2003. Gestation stage-dependent intrauterine trophoblast cell invasion in the rat and mouse: novel endocrine phenotype and regulation. Dev Biol 260:176–190 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

