Absence of hematopoietic tissue factor pathway inhibitor mitigates bleeding in mice with hemophilia
- PMID: 22355108
- PMCID: PMC3309760
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1119858109
Absence of hematopoietic tissue factor pathway inhibitor mitigates bleeding in mice with hemophilia
Abstract
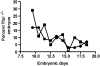
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) blocks thrombin generation via the extrinsic blood coagulation pathway. Because the severe bleeding in patients with hemophilia occurs from deficiency of intrinsic blood coagulation pathway factor VIII or IX, pharmacological agents that inactivate TFPI and, therefore, restore thrombin generation via the extrinsic pathway, are being developed for treatment of hemophilia. Murine models of combined TFPI and factor VIII deficiency were used to examine the impact of TFPI deficiency on bleeding and clotting in hemophilia. In breeding studies, Factor VIII null (F8(-/-)) did not rescue the embryonic death of TFPI null (Tfpi(-/-)) mice. Tfpi(+/-) did not alter the bleeding phenotype of F8(-/-) mice. However, total inhibition of intravascular TFPI through injection of anti-TFPI antibody mitigated tail vein bleeding. Interestingly, tail blood loss progressively decreased at doses greater than needed to totally inhibit plasma TFPI, suggesting that inhibition of a sequestered pool of TFPI released at the injury site mitigates bleeding. Because TFPI is sequestered within platelets and released following their activation, the function of platelet TFPI was examined in F8(-/-) mice lacking hematopoietic cell TFPI that was generated by fetal liver transplantation. Blood loss after tail transection significantly decreased in Tfpi(+/-);F8(-/-) mice with hematopoietic Tfpi(-/-) cells compared with Tfpi(+/-);F8(-/-) mice with Tfpi(+/+) hematopoietic cells. Additionally, following femoral vein injury, Tfpi(+/-);F8(-/-) mice with Tfpi(-/-) hematopoietic cells had increased fibrin deposition compared with identical-genotype mice with Tfpi(+/+) hematopoietic cells. These findings implicate platelet TFPI as a primary physiological regulator of bleeding in hemophilia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.E.M. receives research grant funding from Novo Nordisk. P.B.J., M.B.H., and L.C.P. are employees of Novo Nordisk.
Figures

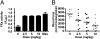

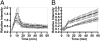
Similar articles
-
Targeting TFPI for hemophilia treatment.Thromb Res. 2016 May;141 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S28-30. doi: 10.1016/S0049-3848(16)30359-0. Thromb Res. 2016. PMID: 27207418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of tissue factor pathway inhibitor isoform beta or gamma, but not alpha, improves clotting in hemophilic mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2024 Oct;22(10):2681-2691. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2024.06.006. Epub 2024 Jun 24. J Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 38925489
-
Murine hematopoietic cell tissue factor pathway inhibitor limits thrombus growth.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Apr;31(4):821-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.220293. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21233452 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer ARC19499 mediates a procoagulant hemostatic effect by inhibiting tissue factor pathway inhibitor.Blood. 2011 May 19;117(20):5514-22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-10-311936. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21389323
-
Revolutionizing Treatment Strategies through Inhibition of Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor: A Promising Therapeutic Approach for Hemophilia Management.J Assoc Physicians India. 2025 Apr;73(4):e47-e54. doi: 10.59556/japi.73.0928. J Assoc Physicians India. 2025. PMID: 40200623 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrauterine lethality in Tfpi gene disrupted mice is differentially suppressed during mid- and late-gestation by platelet TFPIα overexpression.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Jun;19(6):1483-1492. doi: 10.1111/jth.15299. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 33728763 Free PMC article.
-
Activated factor XI increases the procoagulant activity of the extrinsic pathway by inactivating tissue factor pathway inhibitor.Blood. 2015 Feb 26;125(9):1488-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-604587. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25587039 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Blood Clotting and Coagulation Factors in Mice.Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2019 Jun;9(2):e61. doi: 10.1002/cpmo.61. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2019. PMID: 30875463 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Close Future of Hemophilia Treatment - Gene Therapy, TFPI Inhibition, Antithrombin Silencing, and Mimicking Factor VIII with an Engineered Antibody.Transfus Med Hemother. 2018 Apr;45(2):92-96. doi: 10.1159/000488152. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Transfus Med Hemother. 2018. PMID: 29765291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jun;13 Suppl 1(0 1):S200-7. doi: 10.1111/jth.12897. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 26149025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davie EW, Ratnoff OD. Waterfall sequence for intrinsic blood clotting. Science. 1964;145:1310–1312. - PubMed
-
- MacFarlane RG. An enzyme cascade in the blood clotting mechanism, and its function as a biochemical amplifier. Nature. 1964;202:498–499. - PubMed
-
- Broze GJ., Jr The role of tissue factor pathway inhibitor in a revised coagulation cascade. Semin Hematol. 1992;29(3):159–169. - PubMed
-
- Nordfang O, Valentin S, Beck TC, Hedner U. Inhibition of extrinsic pathway inhibitor shortens the coagulation time of normal plasma and of hemophilia plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1991;66:464–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

