Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) is essential for cell division and suppression of DNA re-replication but not for liver regeneration
- PMID: 22355113
- PMCID: PMC3309725
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1115201109
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) is essential for cell division and suppression of DNA re-replication but not for liver regeneration
Abstract
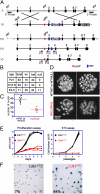
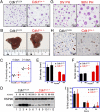
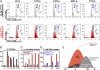
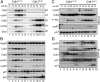
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) is an archetypical kinase and a central regulator that drives cells through G2 phase and mitosis. Knockouts of Cdk2, Cdk3, Cdk4, or Cdk6 have resulted in viable mice, but the in vivo functions of Cdk1 have not been fully explored in mammals. Here we have generated a conditional-knockout mouse model to study the functions of Cdk1 in vivo. Ablation of Cdk1 leads to arrest of embryonic development around the blastocyst stage. Interestingly, liver-specific deletion of Cdk1 is well tolerated, and liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy is not impaired, indicating that regeneration can be driven by cell growth without cell division. The loss of Cdk1 does not affect S phase progression but results in DNA re-replication because of an increase in Cdk2/cyclin A2 activity. Unlike other Cdks, loss of Cdk1 in the liver confers complete resistance against tumorigenesis induced by activated Ras and silencing of p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Morgan DO. The Cell Cycle: Principles of Control. London: New Science Press; 2007.
-
- Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:153–166. - PubMed
-
- Satyanarayana A, Kaldis P. Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: Several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene. 2009;28:2925–2939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

