A 24 kDa excretory-secretory protein of Anisakis simplex larvae could elicit allergic airway inflammation in mice
- PMID: 22355204
- PMCID: PMC3279675
- DOI: 10.3347/kjp.2011.49.4.373
A 24 kDa excretory-secretory protein of Anisakis simplex larvae could elicit allergic airway inflammation in mice
Abstract
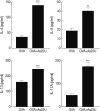
We have reported that a 24 kDa protein (22U homologous; As22U) of Anisakis simplex larvae could elicit several Th2-related chemokine gene expressions in the intestinal epithelial cell line which means that As22U may play a role as an allergen. In order to determine the contribution of As22U to allergic reactions, we treated mice with 6 times intra-nasal application of recombinant As22U (rAs22U). In the group challenged with rAs22U and ovalbumin (OVA), the number of eosinophils in the bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was significantly increased, as compared to the group receiving only OVA. In addition, mice treated with rAs22U and OVA showed significantly increased airway hyperresponsiveness. Thus, severe inflammation around the airway and immune cell recruitment was observed in mice treated with rAs22U plus OVA. The levels of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 cytokines in the BALF increased significantly after treatment with rAs22U and OVA. Similarly, the levels of anti-OVA specific IgE and IgG1 increased in mice treated with rAs22U and OVA, compared to those treated only with OVA. The Gro-α (CXCL1) gene expression in mouse lung epithelial cells increased instantly after treatment with rAs22U, and allergy-specific chemokines eotaxin (CCL11) and thymus-and-activation-regulated-chemokine (CCL17) gene expressions significantly increased at 6 hr after treatment. In conclusion, rAs22U may induce airway allergic inflammation, as the result of enhanced Th2 and Th17 responses.
Keywords: Anisakis simplex; As22U; allergic airway inflammation; excretory secretory protein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Allergenicity of two Anisakis simplex allergens evaluated in vivo using an experimental mouse model.Exp Parasitol. 2014 Nov;146:71-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Exp Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25300761
-
Identification of a 24 kDa excretory secretory protein in Anisakis simplex.Exp Parasitol. 2012 Jan;130(1):69-72. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2011.09.008. Exp Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 22001446
-
Bupleurum chinense extract ameliorates an OVA-induced murine allergic asthma through the reduction of the Th2 and Th17 cytokines production by inactivation of NFκB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jul;91:1085-1095. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.133. Epub 2017 May 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28531919
-
Immune reactions and allergy in experimental anisakiasis.Korean J Parasitol. 2006 Dec;44(4):271-83. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2006.44.4.271. Korean J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 17170569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anisakis simplex: sensitization and clinical allergy.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Jun;5(3):281-5. doi: 10.1097/01.all.0000168795.12701.fd. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15864089 Review.
Cited by
-
Anisakis pegreffii Extract Induces Airway Inflammation with Airway Remodeling in a Murine Model System.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Sep 17;2021:2522305. doi: 10.1155/2021/2522305. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34580637 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of cytokine production during visceral larva migrans by Toxascaris leonina in mice.Korean J Parasitol. 2013 Oct;51(5):583-8. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2013.51.5.583. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Korean J Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 24327787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moreno-Ancillo A, Caballero MT, Cabanas R, Contreras J, Martin-Barroso JA, Barranco P, Lopez-Serrano MC. Allergic reactions to Anisakis simplex parasitizing seafood. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997;79:246–250. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuizen N, Lopata AL, Jeebhay MF, Herbert DR, Robins TG, Brombacher F. Exposure to the fish parasite Anisakis causes allergic airway hyperreactivity and dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:1098–1105. - PubMed
-
- Armentia A, Lombardero M, Callejo A, Martin Santos JM, Gil FJ, Vega J, Arranz ML, Martinez C. Occupational asthma by Anisakis simplex. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102:831–834. - PubMed
-
- Barbuzza O, Guarneri F, Galtieri G, Gangemi S, Vaccaro M. Protein contact dermatitis and allergic asthma caused by Anisakis simplex. Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:239–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

