Mapping and analysis of the LINE and SINE type of repetitive elements in rice
- PMID: 22355220
- PMCID: PMC3280494
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630007276
Mapping and analysis of the LINE and SINE type of repetitive elements in rice
Abstract
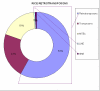
Non-LTR retrotransposons comprise significant portion of the plants genome. Their complete characterization is thus necessary if the sequenced genome is to be annotated correctly. The long and short interspersed nucleotide repetitive elements (LINE and SINE) may be responsible for alteration in the expression mechanism of neighboring genes, the complete identification of these elements in the rice genome is essential in order studying their putative functional interactions with the plant genes and its role in genome composition. The main emphasis of this work is to assemble a comprehensive dataset of nonLTR (LINEs and SINEs) and the map of completely inserted LINEs and SINE type of retroelement by both intact ends (3' and 5' ends). The assembled information and work may help for further research in this direction.
Keywords: LINEs; Oryza sativa; Retroelement; SINEs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RetrOryza: a database of the rice LTR-retrotransposons.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D66-70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl780. Epub 2006 Oct 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17071960 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterisation of Short Interspersed Nuclear Elements in the olive tree (Olea europaea L.) genome.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Feb;292(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1255-3. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27714457
-
[Non-LTR retrotransposons: LINEs and SINEs in plant genome].Yi Chuan. 2006 Jun;28(6):731-6. Yi Chuan. 2006. PMID: 16818439 Review. Chinese.
-
Evolutionary history of Oryza sativa LTR retrotransposons: a preliminary survey of the rice genome sequences.BMC Genomics. 2004 Mar 2;5(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-18. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15040813 Free PMC article.
-
LINEs, SINEs and repetitive DNA: non-LTR retrotransposons in plant genomes.Plant Mol Biol. 1999 Aug;40(6):903-10. doi: 10.1023/a:1006212929794. Plant Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10527415 Review.
Cited by
-
Miniature Inverted-Repeat Transposable Elements: Small DNA Transposons That Have Contributed to Plant MICRORNA Gene Evolution.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;12(5):1101. doi: 10.3390/plants12051101. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of transposable element mPing as a novel genetic tool for modification of the stress response in rice.Mol Breed. 2013;32(3):505-516. doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9885-1. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Mol Breed. 2013. PMID: 24078785 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide occurrence and insertion preferences of INGI/RIME and SLACS CRE transposable elements in Trypanosoma brucei.Mob Genet Elements. 2016 Sep 29;6(6):e1240747. doi: 10.1080/2159256X.2016.1240747. eCollection 2016. Mob Genet Elements. 2016. PMID: 28090379 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Variant Detection by Large-scale Sequencing Reveals New Evolutionary Evidence on Breed Divergence between Chinese and European Pigs.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 5;6:18501. doi: 10.1038/srep18501. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26729041 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
