Integrative analyses of conserved WNT clusters and their co-operative behaviour in human breast cancer
- PMID: 22355234
- PMCID: PMC3280488
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630007339
Integrative analyses of conserved WNT clusters and their co-operative behaviour in human breast cancer
Abstract
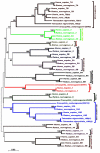
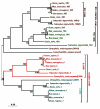
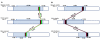
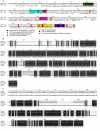
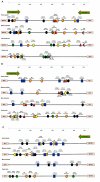
In human, WNT gene clusters are highly conserved at specie level and associated with carcinogenesis. Among them, WNT-10A and WNT-6 genes clustered in chromosome 2q35 are homologous to WNT-10B and WNT-1 located in chromosome 12q13, respectively. In an attempt to study co-regulation, the coordinated expression of these genes was monitored in human breast cancer tissues. As compared to normal tissue, both WNT-10A and WNT-10B genes exhibited lower expression while WNT-6 and WNT-1 showed increased expression in breast cancer tissues. The co-expression pattern was elaborated by detailed phylogenetic and syntenic analyses. Moreover, the intergenic and intragenic regions for these gene clusters were analyzed for studying the transcriptional regulation. In this context, adequate conserved binding sites for SOX and TCF family of transcriptional factors were observed. We propose that SOX9 and TCF4 may compete for binding at the promoters of WNT family genes thus regulating the disease phenotype.
Keywords: SOX; TCF; WNT; breast cancer.
Figures


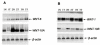

Similar articles
-
WNT and FGF gene clusters (review).Int J Oncol. 2002 Dec;21(6):1269-73. Int J Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12429977 Review.
-
WNT10A and WNT6, clustered in human chromosome 2q35 region with head-to-tail manner, are strongly coexpressed in SW480 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 May 18;283(4):798-805. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4855. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11350055
-
SOX9 and TCF transcription factors associate to mediate Wnt/β-catenin target gene activation in colorectal cancer.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jan;299(1):102735. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102735. Epub 2022 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36423688 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic properties of Tcf1 and Tcf4 splice variants determine cell-type-specific Wnt/β-catenin target gene expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(19):9455-69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks690. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22859735 Free PMC article.
-
TCF: Lady Justice casting the final verdict on the outcome of Wnt signalling.Biol Chem. 2002 Feb;383(2):255-61. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.027. Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11934263 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the wnt1 regulatory chromosomal landscape.Dev Genes Evol. 2019 May;229(2-3):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s00427-019-00629-5. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Dev Genes Evol. 2019. PMID: 30825002 Free PMC article.
-
Stroma as an Active Player in the Development of the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Microenviron. 2015 Dec;8(3):159-66. doi: 10.1007/s12307-014-0150-x. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Cancer Microenviron. 2015. PMID: 25106539 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of structure of human WNT-CRD (FZD) complex for computational drug repurposing.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054630. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372744 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Mammary Gland Development and Offspring's Breast Cancer Risk in Adulthood.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jan 21;14(2):106. doi: 10.3390/biology14020106. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation study of DNA methylation of WNT6 gene with osteosarcoma in children.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):271-275. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6135. Epub 2017 May 8. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693164 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
