Ginkgo biloba: an adjuvant therapy for progressive normal and high tension glaucoma
- PMID: 22355250
- PMCID: PMC3283204
Ginkgo biloba: an adjuvant therapy for progressive normal and high tension glaucoma
Abstract
Gingko biloba has been used for hundreds of years to treat various disorders such as asthma, vertigo, fatigue and, tinnitus or circulatory problems. Two of the main extracts are EGb761 and LI 1370. Most pharmacological, toxicological and clinical studies have focused on the neuroprotective value of these two main extracts. Neuroprotection is a rapidly expanding area of research. This area is of particular interest due to the fact that it represents a new avenue of therapy for a frustrating disease that may progress despite optimal treatment. One such disease is glaucoma.Glaucoma leads to the loss of retinal ganglion cells and their axons but also to tissue remodelling which involves both the optic nerve head and the retina. In the retina the astrocytes get activated. In addition, the optic nerve gets thinner and the cells of the lateral geniculate ganglion disappear partially. On average, ocular blood flow (OBF) is reduced in glaucoma patients in various tissues of the eye. Increased intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major risk factor for glaucomatous damage. Nevertheless, there is little doubt that other risk factors besides IOP are involved. One such risk factor is a primary vascular dysregulation (PVD) occurring in patients with a disturbed autoregulation, another risk factor is oxidative stress.
Figures
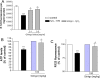

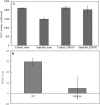
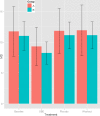
References
-
- Li S, Tang D, Xue Z, Zhang Z, Sun X, Liu Y, Dong H, Yin X, Zhang Z. Biphasic effect of EGb761 on simulated ischemia-induced rat BMSC survival in vitro and in vivo. Life Sci. 2011;88:853–63. - PubMed
-
- Janssen IM, Sturtz S, Skipka G, Zentner A, Garrido MV, Busse R. Ginkgo biloba in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2010;160:539–46. - PubMed
-
- de Lima KC, Schilichting CL, Junior LA, da Silva FM, Benetoli A, Milani H. The Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb 761, fails to reduce brain infarct size in rats after transient, middle cerebral artery occlusion in conditions of unprevented, ischemia-induced fever. Phytother Res. 2006;20:438–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
