Effects of rituximab treatment on the serum concentrations of vitamin D and interleukins 2, 6, 7, and 10 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22355257
- PMCID: PMC3280863
- DOI: 10.2147/BTT.S27840
Effects of rituximab treatment on the serum concentrations of vitamin D and interleukins 2, 6, 7, and 10 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets CD20-positive B-lymphocytes, is used for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with an inadequate response or tolerance to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of rituximab treatment on the serum concentrations of vitamin D, interleukin (IL) 2, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-10 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Forty-five patients, aged 25-78 years, were enrolled into a cohort prospective study. All patients were treated with intravenous rituximab. Disease activity score-28 (DAS-28) and serum concentrations of rheumatoid factor (RF), C-reactive protein (CRP), anticyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), vitamin D, ILs 2, 6, 7, and 10 were estimated in the patients before and after treatment with rituximab.
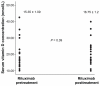
Results: DAS-28, HAQ score, and serum concentrations of CRP, RF, anti-CCP, IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, and ESR significantly decreased after treatment. All 45 patients had vitamin D deficiency before treatment and this did not significantly change after treatment. However no significant association was found among serum vitamin D concentration and any of the ILs.
Conclusion: We concluded from this study that although rituximab treatment of patients with RA significantly reduced their disease activity and serum concentrations of IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, and IL-10, it did not significantly alter their vitamin D status. Furthermore, no significant association was found among serum vitamin D concentration and any of the ILs.
Keywords: interleukins; rheumatoid arthritis; rituximab treatment; vitamin D.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between serum vitamin D Level and disease activity in Thai rheumatoid arthritis patients.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Apr;19(4):355-61. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12222. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 24219063
-
Elevated serum IL-35 levels in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with disease activity.J Investig Med. 2019 Mar;67(3):707-710. doi: 10.1136/jim-2018-000814. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Investig Med. 2019. PMID: 30659089
-
The diagnostic utility of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, matrix metalloproteinase-3, rheumatoid factor, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein in patients with erosive and non-erosive rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Dev Immunol. 2005 Sep;12(3):197-202. doi: 10.1080/17402520500233510. Clin Dev Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16295525 Free PMC article.
-
European multicentre pilot survey to assess vitamin D status in rheumatoid arthritis patients and early development of a new Patient Reported Outcome questionnaire (D-PRO).Autoimmun Rev. 2017 May;16(5):548-554. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28279841 Review.
-
Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis, what is new?J Med Life. 2016 Apr-Jun;9(2):144-8. J Med Life. 2016. PMID: 27453744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BF02, a recombinant TNFR2 fusion protein, alleviates adjuvant arthritis by regulating T lymphocytes in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013 Mar;34(3):414-23. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.171. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013. PMID: 23377547 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D deficiency in patients with either rheumatic diseases or inflammatory bowel diseases on biologic therapy.Intern Emerg Med. 2016 Sep;11(6):803-7. doi: 10.1007/s11739-016-1415-9. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Intern Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 26939587
-
Comparison of the Clinical Efficacy of Rituximab Infusion and Dexamethasone-Cyclophosphamide Pulse Therapy and Their Effect on Serum Th1, Th2, and Th17 Cytokines in Pemphigus Vulgaris-A Prospective, Nonrandomized, Comparative Pilot Study.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024 Apr 29;15(3):464-472. doi: 10.4103/idoj.idoj_558_23. eCollection 2024 May-Jun. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2024. PMID: 38845632 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Dec;3(6):181-7. doi: 10.1177/2042018812471070. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 23323190 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Vitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity: Review and Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 11;11(1):e0146351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146351. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26751969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous