Comparisons of the efficacy of a Jak1/2 inhibitor (AZD1480) with a VEGF signaling inhibitor (cediranib) and sham treatments in mouse tumors using DCE-MRI, DW-MRI, and histology
- PMID: 22355274
- PMCID: PMC3281942
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.111478
Comparisons of the efficacy of a Jak1/2 inhibitor (AZD1480) with a VEGF signaling inhibitor (cediranib) and sham treatments in mouse tumors using DCE-MRI, DW-MRI, and histology
Abstract
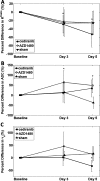
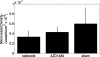
Jak1/2 inhibition suppresses STAT3 phosphorylation that is characteristic of many cancers. Activated STAT3 promotes the transcription of factors that enhance tumor growth, survival, and angiogenesis. AZD1480 is a novel small molecule inhibitor of Jak1/2, which is a key mediator of STAT3 activation. This study examined the use of diffusion-weighted (DW) and dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) biomarkers in assessing early tumor response to AZD1480. Cediranib (AZD2171), a vascular endothelial growth factor signaling inhibitor, was used as a comparator. Thirty mice were injected with Calu-6 lung cancer cells and randomized into the three treatment groups: AZD1480, cediranib, and sham. DW-MRI and DCE-MRI protocols were performed at baseline and at days 3 and 5 after treatment. The percent change from baseline measurements for K(trans), ADC, and v(e) were calculated and compared with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), CD31, cParp, and Ki-67 histology data. Decreases in K(trans) of 29% (P < .05) and 53% (P < .05) were observed at days 3 and 5, respectively, for the cediranib group. No significant changes in K(trans) occurred for the AZD1480 group, but a significant increase in ADC was demonstrated at days 3 (63%, P < .05) and 5 (49%, P < .05). CD31 staining indicated diminished vasculature in the cediranib group, whereas significantly increased cParp staining for apoptotic activity and extracellular space by image analysis of H&E were present in the AZD1480 group. These imaging biomarker changes, and corresponding histopathology, support the use of ADC, but not K(trans), as a pharmacodynamic biomarker of response to AZD1480 at these time points.
Figures

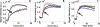





References
-
- Dy GK, Adjei AA. Systemic cancer therapy: evolution over the last 60 years. Cancer. 2008;113:1857–1887. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer—new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2000;19:2474–2488. - PubMed
-
- Niu G, Bowman T, Huang M, Shivers S, Reintgen D, Daud A, Chang A, Kraker A, Jove R, Yu H. Roles of activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth. Oncogene. 2002;21:7001–7010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
