Virologic failures on initial boosted-PI regimen infrequently possess low-level variants with major PI resistance mutations by ultra-deep sequencing
- PMID: 22355307
- PMCID: PMC3280244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030118
Virologic failures on initial boosted-PI regimen infrequently possess low-level variants with major PI resistance mutations by ultra-deep sequencing
Abstract
Background: It is unknown whether HIV-positive patients experiencing virologic failure (VF) on boosted-PI (PI/r) regimens without drug resistant mutations (DRM) by standard genotyping harbor low-level PI resistant variants. CASTLE compared the efficacy of atazanavir/ritonavir (ATV/r) with lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r), each in combination with TVD in ARV-naïve subjects.
Objective: To determine if VF on an initial PI/r-based regimen possess low-level resistant variants that may affect a subsequent PI-containing regimen.
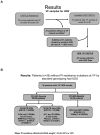
Methods/results: Patients experiencing VF on a Tenofovir/Emtricitabine+PI/r regimen were evaluated by ultra deep sequencing (UDS) for mutations classified/weighted by Stanford HIVdb. Samples were evaluated for variants to 0.4% levels. 36 VF subjects were evaluated by UDS; 24 had UDS for PI and RT DRMs. Of these 24, 19 (79.2%) had any DRM by UDS. The most common UDS-detected DRM were NRTI in 18 subjects: M184V/I (11), TAMs(7) & K65R(4); PI DRMs were detected in 9 subjects: M46I/V(5), F53L(2), I50V(1), D30N(1), and N88S(1). The remaining 12 subjects, all with VLs<10,000, had protease gene UDS, and 4 had low-level PI DRMs: F53L(2), L76V(1), I54S(1), G73S(1). Overall, 3/36(8.3%) subjects had DRMs identified with Stanford-HIVdb weights >12 for ATV or LPV: N88S (at 0.43% level-mutational load 1,828) in 1 subject on ATV; I50V (0.44%-mutational load 110) and L76V (0.52%-mutational load 20) in 1 subject each, both on LPV. All VF samples remained phenotypically susceptible to the treatment PI/r.
Conclusion: Among persons experiencing VF without PI DRMs with standard genotyping on an initial PI/r regimen, low-level variants possessing major PI DRMs were present in a minority of cases, occurred in isolation, and did not result in phenotypic resistance. NRTI DRMs were detected in a high proportion of subjects. These data suggest that PIs may remain effective in subjects experiencing VF on a PI/r-based regimen when PI DRMs are not detected by standard or UDS genotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of minor drug-resistant viral variants in patients experiencing virological failure (VF) on a first-line regimen in Fujian Province by high-throughput sequencing.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):7775-7785. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1347. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353064
-
No impact of HIV-1 protease minority resistant variants on the virological response to a first-line PI-based regimen containing darunavir or atazanavir.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Jan 1;73(1):173-176. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx366. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29077926
-
Impact of low abundance HIV variants on response to ritonavir-boosted atazanavir or fosamprenavir given once daily with tenofovir/emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive HIV-infected patients.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2010 Apr;26(4):407-17. doi: 10.1089/aid.2009.0189. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2010. PMID: 20380480 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Darunavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection in adults.Drugs. 2009;69(4):477-503. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969040-00007. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19323590 Review.
-
[Clinical utility of atazanavir].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008 Dec;26 Suppl 17:55-67. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(08)76622-9. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008. PMID: 20116619 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of a benchtop HIV ultradeep pyrosequencing drug resistance assay in the clinical laboratory.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Mar;51(3):880-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02652-12. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23284027 Free PMC article.
-
MiDRMpol: A High-Throughput Multiplexed Amplicon Sequencing Workflow to Quantify HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutations against Protease, Reverse Transcriptase, and Integrase Inhibitors.Viruses. 2019 Aug 30;11(9):806. doi: 10.3390/v11090806. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31480341 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretroviral therapy and efficacy after virologic failure on first-line boosted protease inhibitor regimens.Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 15;59(6):888-96. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu367. Epub 2014 May 19. Clin Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24842909 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Drug Resistance Mutations (DRMs) Detected by Deep Sequencing in Virologic Failure Subjects on Therapy from Hunan Province, China.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149215. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26895182 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 minority variants to reduced drug susceptibility in patients on an integrase strand transfer inhibitor-based therapy.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 11;9(8):e104512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104512. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25110880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adult and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1 infected adults and adolescents. 2008. Department of Health and Human Services. January 29, 2008; 1–128. Available: http://www.aidsinfo.nih.gov/ContentFiles/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf. Accessed 2010 Aug 22.
-
- Synovate HIV Market Research. all rights reserved. 2009
-
- MacArthur RD, Novak RM, Peng G, Xiang Y, Huppler Hullsiek K, et al. Long-Term Clinical and Immunologic Outcomes Are Similar in HIV-Infected Persons Randomized to NNRTI versus PI versus NNRTI+PI-based Antiretroviral Regimens as Initial Therapy: Results of the CPCRA 058 FIRST Study. LANCET. 2006;368:2125–2135.
-
- Kozal MJ, Hullsiek KHuppler, Macarthur RD, Berg-Wolf M, Peng G, et al. The Incidence of HIV Drug Resistance and Its Impact on Progression of HIV Disease Among Antiretroviral Naïve Participants Started on Three Different Antiretroviral Therapy Strategies. HIV ClinTrials. 2007;6(6):357–370. PMID: 18042501. - PubMed
-
- Molina JM, Andrade-Villanueva J, Echevarria J, Ploenchan C, Corral J, et al. Once-daily atazanavir/ritonavir versus twice-daily lopinavir/ritonavir, each in combination with tenofovir and emtricitabine, for management of antiretroviral-naive HIV-1-infected patients: 48 week efficacy and safety results of the CASTLE study. LANCET. 2008;372(9639):646–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

