A genome wide association scan of bovine tuberculosis susceptibility in Holstein-Friesian dairy cattle
- PMID: 22355315
- PMCID: PMC3280253
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030545
A genome wide association scan of bovine tuberculosis susceptibility in Holstein-Friesian dairy cattle
Abstract
Background: Bovine tuberculosis is a significant veterinary and financial problem in many parts of the world. Although many factors influence infection and progression of the disease, there is a host genetic component and dissection of this may enlighten on the wider biology of host response to tuberculosis. However, a binary phenotype of presence/absence of infection presents a noisy signal for genomewide association study.
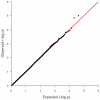
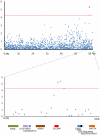
Methodology/principal findings: We calculated a composite phenotype of genetic merit for TB susceptibility based on disease incidence in daughters of elite sires used for artificial insemination in the Irish dairy herd. This robust measure was compared with 44,426 SNP genotypes in the most informative 307 subjects in a genome wide association analysis. Three SNPs in a 65 kb genomic region on BTA 22 were associated (i.e. p<10(-5), peaking at position 59588069, p = 4.02×10(-6)) with tuberculosis susceptibility.
Conclusions/significance: A genomic region on BTA 22 was suggestively associated with tuberculosis susceptibility; it contains the taurine transporter gene SLC6A6, or TauT, which is known to function in the immune system but has not previously been investigated for its role in tuberculosis infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A genome-wide association study for genetic susceptibility to Mycobacterium bovis infection in dairy cattle identifies a susceptibility QTL on chromosome 23.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Mar 9;48:19. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0197-x. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 26960806 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic regions underlying susceptibility to bovine tuberculosis in Holstein-Friesian cattle.BMC Genet. 2017 Mar 23;18(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12863-017-0493-7. BMC Genet. 2017. PMID: 28335717 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci associated with resistance to bovine tuberculosis.Heredity (Edinb). 2014 May;112(5):543-51. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2013.137. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Heredity (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 24496092 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine tuberculosis: the genetic basis of host susceptibility.Proc Biol Sci. 2010 Sep 22;277(1695):2737-45. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2010.0830. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Proc Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20519223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium bovis Infection of Cattle and White-Tailed Deer: Translational Research of Relevance to Human Tuberculosis.ILAR J. 2015;56(1):26-43. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilv001. ILAR J. 2015. PMID: 25991696 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenetic factors affecting susceptibility of humans and rodents to hantaviruses and the clinical course of hantaviral disease in humans.Viruses. 2014 May 26;6(5):2214-41. doi: 10.3390/v6052214. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 24859344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Genomic Tools to Improve Cattle Health in the Context of Infectious Diseases.Front Genet. 2016 Mar 7;7:30. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00030. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27014337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and risk factors of mycobacterial infections in farm and trade cattle in southwestern Nigeria.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2018 Apr;50(4):761-772. doi: 10.1007/s11250-017-1492-4. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2018. PMID: 29274054
-
Risk factors and true prevalence of bovine tuberculosis in Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 26;16(2):e0247838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247838. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33635911 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics and disease resistance studies in livestock.Livest Sci. 2014 Aug;166:190-198. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2014.04.034. Livest Sci. 2014. PMID: 26339300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perry BD, Randolph TF, McDermott JJ, Sones KR, Thornton PK. Investing in Animal Health Research to Alleviate Poverty. Nairobi: ILRI (International Livestock Research Institute); 2002.
-
- Hewinson RG, Vordermeier HM, Smith NH, Gordon SV. Recent advances in our knowledge of Mycobacterium bovis: a feeling for the organism. Vet Microbiol. 2006;112:127–139. - PubMed
-
- Sheridan M. Progress in tuberculosis eradication in Ireland. Vet Microbiol. 2011;151:160–169. - PubMed
-
- Smith NH, Berg S, Dale J, Allen A, Rodriguez S, et al. European 1: A globally important clonal complex of Mycobacterium bovis. Infect Genet Evol 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

