IGD motifs, which are required for migration stimulatory activity of fibronectin type I modules, do not mediate binding in matrix assembly
- PMID: 22355321
- PMCID: PMC3280255
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030615
IGD motifs, which are required for migration stimulatory activity of fibronectin type I modules, do not mediate binding in matrix assembly
Abstract
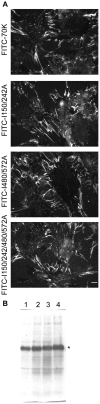
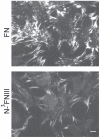
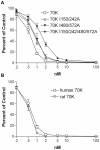
Picomolar concentrations of proteins comprising only the N-terminal 70-kDa region (70K) of fibronectin (FN) stimulate cell migration into collagen gels. The Ile-Gly-Asp (IGD) motifs in four of the nine FN type 1 (FNI) modules in 70K are important for such migratory stimulating activity. The 70K region mediates binding of nanomolar concentrations of intact FN to cell-surface sites where FN is assembled. Using baculovirus, we expressed wildtype 70K and 70K with Ile-to-Ala mutations in (3)FNI and (5)FNI; (7)FNI and (9)FNI; or (3)FNI, (5)FNI, (7)FNI, and (9)FNI. Wildtype 70K and 70K with Ile-to-Ala mutations were equally active in binding to assembly sites of FN-null fibroblasts. This finding indicates that IGD motifs do not mediate the interaction between 70K and the cell-surface that is important for FN assembly. Further, FN fragment N-(3)FNIII, which does not stimulate migration, binds to assembly sites on FN-null fibroblast. The Ile-to-Ala mutations had effects on the structure of FNI modules as evidenced by decreases in abilities of 70K with Ile-to-Ala mutations to bind to monoclonal antibody 5C3, which recognizes an epitope in (9)FNI, or to bind to FUD, a polypeptide based on the F1 adhesin of Streptococcus pyogenes that interacts with 70K by the β-zipper mechanism. These results suggest that the picomolar interactions of 70K with cells that stimulate cell migration require different conformations of FNI modules than the nanomolar interactions required for assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- George EL, Georges-Labouesse EN, Patel-King RS, Rayburn H, Hynes RO. Defects in mesoderm, neural tube and vascular development in mouse embryos lacking fibronectin. Development. 1993;119:1079–1091. - PubMed
-
- Pankov R, Yamada KM. Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3861–3863. - PubMed
-
- Zerlauth G, Wolf G. Plasma fibronectin as a marker for cancer and other diseases. Am J Med. 1984;77:685–689. - PubMed
-
- Cho J, Mosher DF. Role of fibronectin assembly in platelet thrombus formation. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:1461–1469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

