Posture as index for approach-avoidance behavior
- PMID: 22355355
- PMCID: PMC3280282
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031291
Posture as index for approach-avoidance behavior
Abstract
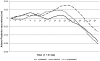
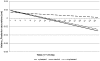
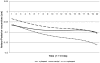
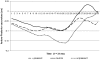
Approach and avoidance are two behavioral responses that make people tend to approach positive and avoid negative situations. This study examines whether postural behavior is influenced by the affective state of pictures. While standing on the Wii™ Balance Board, participants viewed pleasant, neutral, and unpleasant pictures (passively viewing phase). Then they had to move their body to the left or the right (lateral movement phase) to make the next picture appear. We recorded movements in the anterior-posterior direction to examine approach and avoidant behavior. During passively viewing, people approached pleasant pictures. They avoided unpleasant ones while they made a lateral movement. These findings provide support for the idea that we tend to approach positive and avoid negative situations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of affective picture viewing on postural control.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Oct 4;8:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-83. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17916245 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion and motivated behavior: postural adjustments to affective picture viewing.Biol Psychol. 2004 Mar;66(1):51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2003.07.005. Biol Psychol. 2004. PMID: 15019170
-
A freezing-like posture to pictures of mutilation.Psychophysiology. 2005 May;42(3):255-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00287.x. Psychophysiology. 2005. PMID: 15943678 Clinical Trial.
-
Emotional state affects the initiation of forward gait.Emotion. 2011 Apr;11(2):267-77. doi: 10.1037/a0022577. Emotion. 2011. PMID: 21500896
-
Head movement measurement: An alternative method for posturography studies.Gait Posture. 2017 Feb;52:100-106. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Gait Posture. 2017. PMID: 27888694 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between oxytocin and maternal approach behaviors to infants' vocalizations.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2020 Sep 19;4:100010. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2020.100010. eCollection 2020 Nov. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2020. PMID: 35755631 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of cardiac synchronisation on self-attribution to external objects in male participants.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1442942. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1442942. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39282685 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping distance or getting closer: How others' emotions shape approach-avoidance postural behaviors and preferred interpersonal distance.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 2;19(2):e0298069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298069. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38306322 Free PMC article.
-
Stepping into emotions: investigating the effect of angry and fearful faces on forward stepping and quiet stance.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Aug 9;18:1411246. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1411246. eCollection 2024. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39183817 Free PMC article.
-
Current research topics in embodied social cognition.Cogn Process. 2014 Aug;15(3):235-6. doi: 10.1007/s10339-014-0624-2. Epub 2014 Jul 20. Cogn Process. 2014. PMID: 25039010 No abstract available.
References
-
- Frijda NH. The Emotions. London: Cambridge University Press; 1986.
-
- Elliot AJ, Covington MV. Approach and avoidance motivation. Educ Psychol Rev. 2001;13:73–92.
-
- Rutherford HJV, Lindell AK. Thriving and surviving: Approach and avoidance motivation and lateralization. Emotion Rev. 2011;3:333–343.
-
- Solarz A. Latency of instrumental responses as a function of compatibility with the meaning of eliciting verbal signs. J Exp Psychol. 1960;59:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Bargh J, Chartrand T. The unbearable automaticity of being. Am Psychol. 1999;54:462–479.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

