Hepatitis B virus X protein drives multiple cross-talk cascade loops involving NF-κB, 5-LOX, OPN and Capn4 to promote cell migration
- PMID: 22355367
- PMCID: PMC3280298
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031458
Hepatitis B virus X protein drives multiple cross-talk cascade loops involving NF-κB, 5-LOX, OPN and Capn4 to promote cell migration
Abstract
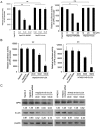
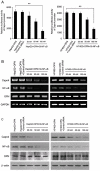
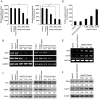
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays an important role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanism remains unclear. Recently, we have reported that HBx promotes hepatoma cell migration through the upregulation of calpain small subunit 1 (Capn4). In addition, several reports have revealed that osteopontin (OPN) plays important roles in tumor cell migration. In this study, we investigated the signaling pathways involving the promotion of cell migration mediated by HBx. We report that HBx stimulates several factors in a network manner to promote hepatoma cell migration. We showed that HBx was able to upregulate the expression of osteopontin (OPN) through 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) in HepG2-X/H7402-X (stable HBx-transfected cells) cells. Furthermore, we identified that HBx could increase the expression of 5-LOX through nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). We also found that OPN could upregulate Capn4 through NF-κB. Interestingly, we showed that Capn4 was able to upregulate OPN through NF-κB in a positive feedback manner, suggesting that the OPN and Capn4 proteins involving cell migration affect each other in a network through NF-κB. Importantly, NF-κB plays a crucial role in the regulation of 5-LOX, OPN and Capn4. Thus, we conclude that HBx drives multiple cross-talk cascade loops involving NF-κB, 5-LOX, OPN and Capn4 to promote cell migration. This finding provides new insight into the mechanism involving the promotion of cell migration by HBx.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Feitelson MA, Sun B, Satiroglu Tufan NL, Liu J, Pan J, et al. Genetic mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2002;21:2593–2604. - PubMed
-
- Lee YM, Kang M, Hwang JM, Lee S, Cho H, et al. Sulfasalazine induces apoptosis of HBx-expressing cells in an NF-kappaB-independent manner. Virus Genes. 2010;40:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JL, Zhao WG, Wu KL, Wang K, Zhang X, et al. Human hepatitis B virus X protein promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis through interacting with a serine protease Hepsin. Arch Virol. 2005;150:721–741. - PubMed
-
- Lara-Pezzi E, Majano PL, Yanez-Mo M, Gomez-Gonzalo M, Carretero M, et al. Effect of the hepatitis B virus HBx protein on integrin-mediated adhesion to and migration on extracellular matrix. J Hepatol. 2001;34:409–415. - PubMed
-
- Lara-Pezzi E, Serrador JM, Montoya MC, Zamora D, Yanez-Mo M, et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) induces a migratory phenotype in a CD44-dependent manner: possible role of HBx in invasion and metastasis. Hepatology. 2001;33:1270–1281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

