Reduced Retinal Function in the Absence of Na(v)1.6
- PMID: 22355369
- PMCID: PMC3280295
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031476
Reduced Retinal Function in the Absence of Na(v)1.6
Abstract
Background: Mice with a function-blocking mutation in the Scn8a gene that encodes Na(v)1.6, a voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC) isoform normally found in several types of retinal neurons, have previously been found to display a profoundly abnormal dark adapted flash electroretinogram. However the retinal function of these mice in light adapted conditions has not been studied.
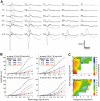
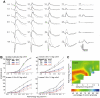
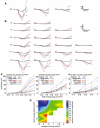
Methodology/principal findings: In the present report we reveal that during light adaptation these animals are shown to have electroretinograms with significant decreases in the amplitude of the a- and b-waves. The percent decrease in the a- and b-waves substantially exceeds the acute effect of VGSC block by tetrodotoxin in control littermates. Intravitreal injection of CoCl(2) or CNQX to isolate the a-wave contributions of the photoreceptors in littermates revealed that at high background luminance the cone-isolated component of the a-wave is of the same amplitude as the a-wave of mutants.
Conclusions/significance: Our results indicate that Scn8a mutant mice have reduced function in both rod and the cone retinal pathways. The extent of the reduction in the cone pathway, as quantified using the ERG b-wave, exceeds the reduction seen in control littermates after application of TTX, suggesting that a defect in cone photoreceptors contributes to the reduction. Unless the postreceptoral component of the a-wave is increased in Scn8a mutant mice, the reduction in the b-wave is larger than can be accounted for by reduced photoreceptor function alone. Our data suggests that the reduction in the light adapted ERG of Scn8a mutant mice is caused by a combination of reduced cone photoreceptor function and reduced depolarization of cone ON bipolar cells. This raises the possibility that Na(v)1.6 augments signaling in cone bipolar cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Contribution of voltage-gated sodium channels to the b-wave of the mammalian flash electroretinogram.J Physiol. 2008 May 15;586(10):2551-80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.150755. Epub 2008 Apr 3. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18388140 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated sodium channel alpha-subunits Na(v)1.1, Na(v)1.2, and Na(v)1.6 in the distal mammalian retina.Mol Vis. 2007 Nov 27;13:2163-82. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 18079688
-
Contribution of voltage-gated sodium channels to b- and d-waves of frog electroretinogram under different conditions of light adaptation.Vision Res. 2010 Jan;50(1):88-98. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.10.015. Vision Res. 2010. PMID: 19854212
-
Human retinal dark adaptation tracked in vivo with the electroretinogram: insights into processes underlying recovery of cone- and rod-mediated vision.J Physiol. 2022 Nov;600(21):4603-4621. doi: 10.1113/JP283105. Epub 2022 Jun 7. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35612091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuning outer segment Ca2+ homeostasis to phototransduction in rods and cones.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:179-203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596922 Review.
Cited by
-
Voltage- and calcium-gated ion channels of neurons in the vertebrate retina.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019 Sep;72:100760. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 May 10. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31078724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of retinal ganglion cells to the mouse electroretinogram.Doc Ophthalmol. 2014 Jun;128(3):155-68. doi: 10.1007/s10633-014-9433-2. Doc Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24659322
-
Cisplatin-Induced Toxic Optic Neuropathy in a Patient With Hodgkin's Lymphoma.Cureus. 2024 Sep 10;16(9):e69140. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69140. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39398796 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the modulation of the neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1.6 by calmodulin.Sci Rep. 2013;3:2435. doi: 10.1038/srep02435. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23942337 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

