The actin cytoskeleton as a barrier to virus infection of polarized epithelial cells
- PMID: 22355449
- PMCID: PMC3280511
- DOI: 10.3390/v3122462
The actin cytoskeleton as a barrier to virus infection of polarized epithelial cells
Abstract
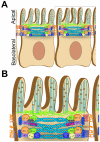
Many diverse viruses target a polarized epithelial monolayer during host invasion. The polarized epithelium is adept at restricting the movement of solutes, ions, macromolecules, and pathogens across the mucosa. This regulation can be attributed to the presence of a junctional complex between adjacent cells and to an intricate network of actin filaments that provides support to the subapical membrane and stabilizes intercellular junctions. It is therefore not surprising that many viruses have evolved highly varied strategies to dissolve or modulate the cortical actin meshwork to promote infection of polarized cells. In this review, we will discuss the cell biological properties of the actin cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells and review the known mechanisms utilized by viral pathogens to manipulate this system in order to facilitate their infection.
Keywords: actin cytoskeleton; polarized epithelium; tight junctions; virus entry.
Figures
References
-
- Gibson M.C., Perrimon N. Apicobasal polarization: Epithelial form and function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2003;15:747–752. - PubMed
-
- Wedlich-Soldner R., Li R. Closing the loops: New insights into the role and regulation of actin during cell polarization. Exp. Cell Res. 2004;301:8–15. - PubMed
-
- Saotome I., Curto M., McClatchey A.I. Ezrin is essential for epithelial organization and villus morphogenesis in the developing intestine. Dev. Cell. 2004;6:855–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

