Riboflavin alleviates cardiac failure in Type I diabetic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 22355488
- PMCID: PMC3282438
- DOI: 10.4081/hi.2011.e21
Riboflavin alleviates cardiac failure in Type I diabetic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
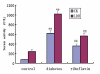
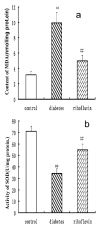
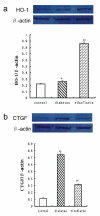
Heart failure (HF) is a common and serious comorbidity of diabetes. Oxidative stress has been associated with the pathogenesis of chronic diabetic complications including cardiomyopathy. The ability of antioxidants to inhibit injury has raised the possibility of new therapeutic treatment for diabetic heart diseases. Riboflavin constitutes an essential nutrient for humans and animals and it is an important food additive. Riboflavin, a precursor of flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), enhances the oxidative folding and subsequent secretion of proteins. The objective of this study was to investigate the cardioprotective effect of riboflavin in diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced in 30 rats by a single injection of streptozotocin (STZ) (70 mg /kg). Riboflavin (20 mg/kg) was orally administered to animals immediately after induction of diabetes and was continued for eight weeks. Rats were examined for diabetic cardiomyopathy by left ventricular (LV) remadynamic function. Myocardial oxidative stress was assessed by measuring the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), the level of malondialdehyde (MDA) as well as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) protein level. Myocardial connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) level was measured by Western blot in all rats at the end of the study. In the untreated diabetic rats, left ventricular systolic pressure (LVSP) rate of pressure rose (+dp/dt), and rate of pressure decay (-dp/dt) were depressed while left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) was increased, which indicated the reduced left ventricular contractility and slowing of left ventricular relaxation. The level of SOD decreased, CTGF and HO-1 protein expression and MDA content rose. Riboflavin treatment significantly improved left ventricular systolic and diastolic function in diabetic rats, there were persistent increases in significant activation of SOD and the level of HO-1 protein, and a decrease in the level of CTGF. These results suggest that riboflavin treatment ameliorates myocardial function and improves heart oxidant status, whereas raising myocardial HO-1 and decreasing myocardial CTGF levels have beneficial effects on diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: diabetic cardiomyopathy; heme oxygenase-1.; riboflavin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115:3213–23. - PubMed
-
- Nishiya D, Enomoto S, Omura T, et al. The long-acting Ca2+-channel blocker azelnidipine prevents left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. J Pharmacol Sci. 2007;103:391–7. - PubMed
-
- Hussain MJ, Peakman M, Gallati H, et al. Elevated serum levels of macrophage-derived cytokines precede and accompany the onset of IDDM. Diabetologia. 1996;39:60–9. - PubMed
-
- Kini AS, Kim MC, Moreno PR, et al. Comparison of coronary flow reserve and fractional flow reserve in patients with versus without diabetes mellitus and having elective percutaneous coronary intervention and abciximab therapy (from the PREDICT Trial) Am J Cardiol. 2008;101:796–800. - PubMed
-
- Geddes J, Deans KA, Cormack A, et al. Cardiac troponin I concentrations in people presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis. Ann Clin Biochem. 2007;44:391–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
