Differential macrophage polarization promotes tissue remodeling and repair in a model of ischemic retinopathy
- PMID: 22355595
- PMCID: PMC3216563
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00076
Differential macrophage polarization promotes tissue remodeling and repair in a model of ischemic retinopathy
Abstract
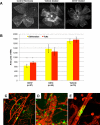
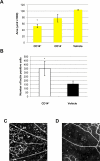
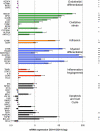
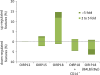
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of visual loss in individuals under the age of 55. Umbilical cord blood (UCB)-derived myeloid progenitor cells have been shown to decrease neuronal damage associated with ischemia in the central nervous system. In this study we show that UCB-derived CD14(+) progenitor cells provide rescue effects in a mouse model of ischemic retinopathy by promoting physiological angiogenesis and reducing associated inflammation. We use confocal microscopy to trace the fate of injected human UCB-derived CD14(+) cells and PCR with species-specific probes to investigate their gene expression profile before and after injection. Metabolomic analysis measures changes induced by CD14(+) cells. Our results demonstrate that human cells differentiate in vivo into M2 macrophages and induce the polarization of resident M2 macrophages. This leads to stabilization of the ischemia-injured retinal vasculature by modulating the inflammatory response, reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis and promoting tissue repair.
Figures
References
-
- Roncarolo M. G., Bigler M., Ciuti E., Martino S. & Tovo P. A. Immune responses by cord blood cells. Blood Cells 20, 573–585; discussion 585–576 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Henning R. J. et al.. Human cord blood cells and myocardial infarction: effect of dose and route of administration on infarct size. Cell Transplant 16, 907–917 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Womble T. A., Green S., Sanberg P. R., Pennypacker K. R. & Willing A. E. CD14(+) human umbilical cord blood cells are essential for neurological recovery following MCAO. Cell Transplantation 17, 485–486 (2008).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

