Defining the tipping point: a complex cellular life/death balance in corals in response to stress
- PMID: 22355675
- PMCID: PMC3240979
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00160
Defining the tipping point: a complex cellular life/death balance in corals in response to stress
Abstract
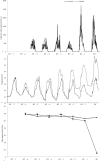
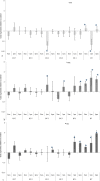
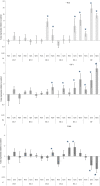
Apoptotic cell death has been implicated in coral bleaching but the molecules involved and the mechanisms by which apoptosis is regulated are only now being identified. In contrast the mechanisms underlying apoptosis in higher animals are relatively well understood. To better understand the response of corals to thermal stress, the expression of coral homologs of six key regulators of apoptosis was studied in Acropora aspera under conditions simulating those of a mass bleaching event. Significant changes in expression were detected between the daily minimum and maximum temperatures. Maximum daily temperatures from as low as 3°C below the bleaching threshold resulted in significant changes in both pro- and anti-apoptotic gene expression. The results suggest that the control of apoptosis is highly complex in this eukaryote-eukaryote endosymbiosis and that apoptotic cell death cascades potentially play key roles tipping the cellular life/death balance during environmental stress prior to the onset of coral bleaching.
Figures

References
-
- Mumby P. J. & Steneck R. S. in Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition eds Zvy Dubinsky, & Noga Stambler) 509–519 (Springer Netherlands, 2011).
-
- Hoegh-Guldberg O. Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world's coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 50, 839–866 (1999).
-
- Brown B. E. Coral bleaching: causes and consequences. Coral Reefs 16, s129–s138 (1997).
-
- Weis V. M. Cellular mechanisms of Cnidarian bleaching: stress causes the collapse of symbiosis. Journal of Experimental Biology 211, 3059–3066 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Baird A. H., Bhagooli R., Ralph P. J. & Takahashi S. Coral bleaching: the role of the host. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24, 16–20 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

