The precision of axon targeting of mouse olfactory sensory neurons requires the BACE1 protease
- PMID: 22355745
- PMCID: PMC3262176
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00231
The precision of axon targeting of mouse olfactory sensory neurons requires the BACE1 protease
Abstract
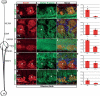
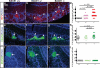
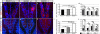
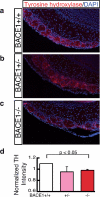
The β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) is necessary to generate the Aβ peptide, which is implicated in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Studies show that the expression of BACE1 and its protease activity are tightly regulated, but the physiological function of BACE1 remains poorly understood. Recently, numerous axon guidance proteins were identified as potential substrates of BACE1. Here, we examined the consequences of loss of BACE1 function in a well-defined in vivo model system of axon guidance, mouse olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs). The BACE1 protein resides predominantly in proximal segment and the termini of OSN axons, and the expression of BACE1 inversely correlates with odor-evoked neural activity. The precision of targeting of OSN axons is disturbed in both BACE1 null and, surprisingly, in BACE1 heterozygous mice. We propose that BACE1 cleavage of axon guidance proteins is essential to maintain the connectivity of OSNs in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Vassar R. et al. Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286, 735–741 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Hussain I. et al. Identification of a novel aspartic protease (Asp 2) as beta-secretase. Mol Cell Neurosci 14, 419–427 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

