An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication
- PMID: 22355771
- PMCID: PMC3277087
- DOI: 10.1038/srep00259
An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication
Abstract
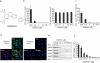
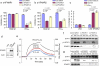
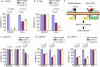
Most acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections become chronic and some progress to liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma. Standard therapy involves an interferon (IFN)-α-based regimen, and efficacy of therapy has been significantly improved by the development of protease inhibitors. However, several issues remain concerning the injectable form and the side effects of IFN. Here, we report an orally available, small-molecule type I IFN receptor agonist that directly transduces the IFN signal cascade and stimulates antiviral gene expression. Like type I IFN, the small-molecule compound induces IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) expression for antiviral activity in vitro and in vivo in mice, and the ISG induction mechanism is attributed to a direct interaction between the compound and IFN-α receptor 2, a key molecule of IFN-signaling on the cell surface. Our study highlights the importance of an orally active IFN-like agent, both as a therapy for antiviral infections and as a potential IFN substitute.
Figures

References
-
- Lavanchy D. The global burden of hepatitis. Liver Int. 29, 74–81 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Zeuzem S. Interferon-based therapy for chronic hepatitis C: current and future perspectives. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5, 610–622 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Ge D. et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature. 461, 399–401 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Suppiah V. et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet. 41, 1100–4 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

