Statin-dependent activation of protein kinase Cδ in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and induction of leukemic cell differentiation
- PMID: 22356114
- PMCID: PMC3616499
- DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2012.668287
Statin-dependent activation of protein kinase Cδ in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and induction of leukemic cell differentiation
Abstract
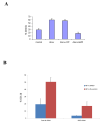
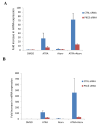
Statins are HMG-CoA (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A) reductase inhibitors, which block the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate and have potent cholesterol lowering properties. Beyond their importance in the generation of lipid lowering effects, the regulatory effects of statins on the mevalonate pathway have a significant impact on multiple other cellular functions. There is now extensive evidence that statins have anti-inflammatory and anti-neoplastic properties, but the precise mechanisms by which such responses are generated are not well understood. In the present study we demonstrate that statins engage a member of the protein kinase C (PKC) family of proteins, PKCδ, in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells. Our study shows that atorvastatin and fluvastatin induce proteolytic activation of PKCδ in the APL NB4 cell line, which expresses the t(15;17) translocation. Such engagement of PKCδ results in induction of its kinase domain and downstream regulation of pathways important for statin-dependent leukemia cell differentiation. Our research shows that the function of PKCδ is essential for statin-induced leukemic cell differentiation, as demonstrated by studies involving selective targeting of PKCδ using siRNAs. We also demonstrate that the potent enhancing effects of statins on all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced gene expression for CCL3 and CCL4 requires the function of PKCδ, suggesting a mechanism by which statins may promote ATRA-induced antileukemic responses. Altogether, our data establish a novel function for PKCδ as a mediator of statin-induced differentiation of APL cells and antileukemic effects.
Figures
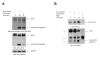

Similar articles
-
Suppressive effects of statins on acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):4524-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3686. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483369
-
Regulation of leukemic cell differentiation and retinoid-induced gene expression by statins.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Mar;8(3):615-25. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-1196. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19240159 Free PMC article.
-
Statins and fenofibrate affect skeletal muscle chloride conductance in rats by differently impairing ClC-1 channel regulation and expression.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;156(8):1206-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00079.x. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19220292 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins.Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Dec;84(3):413-28. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(99)00045-5. Pharmacol Ther. 1999. PMID: 10665838 Review.
-
The clinical relevance of low-density-lipoproteins size modulation by statins.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006 Jun;20(3):205-17. doi: 10.1007/s10557-006-8283-x. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006. PMID: 16775666 Review.
Cited by
-
All-trans retinoic acid and protein kinase C α/β1 inhibitor combined treatment targets cancer stem cells and impairs breast tumor progression.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 15;11(1):6044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85344-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33723318 Free PMC article.
-
Human thrombopoiesis depends on Protein kinase Cδ/protein kinase Cε functional couple.Haematologica. 2016 Jul;101(7):812-20. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.137984. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Haematologica. 2016. PMID: 27081176 Free PMC article.
-
6-Formylindolo (3,2-b)carbazole (FICZ) enhances retinoic acid (RA)-induced differentiation of HL-60 myeloblastic leukemia cells.Mol Cancer. 2013 May 9;12:39. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-39. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23656719 Free PMC article.
-
Statin-specific inhibition of Rab-GTPase regulates cPKC-mediated IKs internalization.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 28;9(1):17747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53700-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31780674 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin Enhances Activity and Trafficking of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor in Hippocampal Neurons Through PKC and CaMKII Signaling Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 12;9:362. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00362. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29706890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sassano A, Platanias LC. Statins in tumor suppression. Cancer Lett. 2008;260:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Khurana V, Caldito G, Ankem M. Statins might reduce risk of renal cell carcinoma in humans: case-control study of 500,000 veterans. Urology. 2008;71:118–122. - PubMed
-
- Khurana V, Bejjanki HR, Caldito G, Owens MW. Statins reduce the risk of lung cancer in humans: a large case-control study of US veterans. Chest. 2007;131:1282–1288. - PubMed
-
- Khurana V, Sheth A, Caldito G, Barkin JS. Statins reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer in humans: a case-control study of half a million veterans. Pancreas. 2007;34:260. - PubMed
-
- Woodard J, Sassano A, Hay N, Platanias LC. Statin-dependent suppression of the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling cascade and programmed cell death 4 up-regulation in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:4640–4649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
