A novel zebrafish embryo xenotransplantation model to study primary human fibroblast motility in health and disease
- PMID: 22356695
- PMCID: PMC3308709
- DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2011.0705
A novel zebrafish embryo xenotransplantation model to study primary human fibroblast motility in health and disease
Abstract
Fibroblasts have a central role in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and repair after injury. Currently, there are no tractable, cost-effective model systems for studying the biology of human fibroblasts in vivo. Here we demonstrate that primary human fibroblasts survive transplantation into zebrafish embryos. Transplanted cells migrate and proliferate, but do not integrate into host tissues. We used this system to study the intrinsic motility of lung fibroblasts from a prototype fibrotic lung disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). IPF fibroblasts displayed a significantly higher level of motility than did fibroblasts from nonfibrotic lungs. This is the first in vivo examination of primary human lung fibroblast motility in health and disease using zebrafish models.
Figures


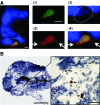

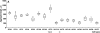
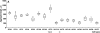
Similar articles
-
The fate of human malignant melanoma cells transplanted into zebrafish embryos: assessment of migration and cell division in the absence of tumor formation.Dev Dyn. 2005 Aug;233(4):1560-70. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20471. Dev Dyn. 2005. PMID: 15968639
-
Enhanced migration of fibroblasts derived from lungs with fibrotic lesions.Thorax. 1995 Sep;50(9):984-9. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.9.984. Thorax. 1995. PMID: 8539681 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids induce activation of alveolar epithelial cells and lung fibroblasts through farnesoid X receptor-dependent and independent pathways.Respirology. 2016 Aug;21(6):1075-80. doi: 10.1111/resp.12815. Epub 2016 May 17. Respirology. 2016. PMID: 27185272
-
The study of glioma by xenotransplantation in zebrafish early life stages.J Histochem Cytochem. 2015 Oct;63(10):749-61. doi: 10.1369/0022155415595670. Epub 2015 Jun 24. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015. PMID: 26109632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-TGF-beta 1 crosstalk in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: autocrine mechanisms in myofibroblasts and macrophages.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(12):1247-56. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618885. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17504233 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin E2 promotes embryonic vascular development and maturation in zebrafish.Biol Open. 2019 Apr 18;8(4):bio039768. doi: 10.1242/bio.039768. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 30890523 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a cell-of-origin for fibroblasts comprising the fibrotic reticulum in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2014 May;184(5):1369-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.01.012. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24631025 Free PMC article.
-
Animals devoid of pulmonary system as infection models in the study of lung bacterial pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2015 Feb 4;6:38. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00038. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25699030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative approaches to establish and characterize primary cultures: an ex vivo 3D system and the zebrafish model.Biol Open. 2017 Feb 15;6(2):133-140. doi: 10.1242/bio.022483. Biol Open. 2017. PMID: 27895047 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia enhances IPF mesenchymal progenitor cell fibrogenicity via the lactate/GPR81/HIF1α pathway.JCI Insight. 2023 Feb 22;8(4):e163820. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.163820. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 36656644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C. Of flies and fishes. Science. 1994;266:572–574. - PubMed
-
- Stern HM. Zon LI. Cancer genetics and drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:533–539. - PubMed
-
- Kari G. Rodeck U. Dicker AP. Zebrafish: An emerging model system for human disease and drug discovery. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;82:70–80. - PubMed
-
- Feitsma H. Cuppen E. Zebrafish as a cancer model. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:685–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

