Location, location, location: the BRMS1 protein and melanoma progression
- PMID: 22356729
- PMCID: PMC3298489
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-19
Location, location, location: the BRMS1 protein and melanoma progression
Abstract
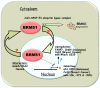
The metastasis suppressor, BRMS1, has been demonstrated to cause dramatic regression of metastatic lesions without blocking orthotopic tumor growth. The role of BRMS1 is well-documented for several non-melanoma malignancies, such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer and non-small-cell lung cancer. However, its role in melanoma is just beginning to be understood, with a recent article by Slipicevic et al. highlighting the levels of expression of BRMS1 in benign nevi, primary and metastatic melanoma samples. Their findings emphasize that the intracellular location of BRMS1 protein (cytoplasmic or nuclear), appears to have a significant impact upon the metastatic capacity of melanoma cells. Interestingly, this selective localization translates into a statistically significant decrease in the relapse-free period in melanoma patients, further associated with a thicker Breslow's depth of primary melanomas. However, and more importantly, this study begins to define a clearer role for BRMS1 in melanoma that is strictly dependent upon its cellular location, with nuclear expression associated with invasive and metastatic capacity and cytoplasmic expression resulting in repressive effects upon progression and metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Samant RS, Seraj MJ, Saunders MM, Sakamaki TS, Shevde LA, Harms JF, Leonard TO, Goldberg SF, Budgeon L, Meehan WJ, Winter CR, Christensen ND, Verderame MF, Donahue HJ, Welch DR. Analysis of mechanisms underlying BRMS1 suppression of metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2000;18:683–693. doi: 10.1023/A:1013124725690. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seraj MJ, Samant RS, Verderame MF, Welch DR. Functional evidence for a novel human breast carcinoma metastasis suppressor, BRMS1, encoded at chromosome 11q13. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2764–2769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

