A pharmacist-led information technology intervention for medication errors (PINCER): a multicentre, cluster randomised, controlled trial and cost-effectiveness analysis
- PMID: 22357106
- PMCID: PMC3328846
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61817-5
A pharmacist-led information technology intervention for medication errors (PINCER): a multicentre, cluster randomised, controlled trial and cost-effectiveness analysis
Erratum in
- Lancet. 2012 Jun 16;379(9833):2242
Abstract
Background: Medication errors are common in primary care and are associated with considerable risk of patient harm. We tested whether a pharmacist-led, information technology-based intervention was more effective than simple feedback in reducing the number of patients at risk of measures related to hazardous prescribing and inadequate blood-test monitoring of medicines 6 months after the intervention.
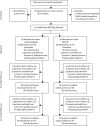
Methods: In this pragmatic, cluster randomised trial general practices in the UK were stratified by research site and list size, and randomly assigned by a web-based randomisation service in block sizes of two or four to one of two groups. The practices were allocated to either computer-generated simple feedback for at-risk patients (control) or a pharmacist-led information technology intervention (PINCER), composed of feedback, educational outreach, and dedicated support. The allocation was masked to researchers and statisticians involved in processing and analysing the data. The allocation was not masked to general practices, pharmacists, patients, or researchers who visited practices to extract data. [corrected]. Primary outcomes were the proportions of patients at 6 months after the intervention who had had any of three clinically important errors: non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) prescribed to those with a history of peptic ulcer without co-prescription of a proton-pump inhibitor; β blockers prescribed to those with a history of asthma; long-term prescription of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or loop diuretics to those 75 years or older without assessment of urea and electrolytes in the preceding 15 months. The cost per error avoided was estimated by incremental cost-effectiveness analysis. This study is registered with Controlled-Trials.com, number ISRCTN21785299.
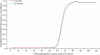
Findings: 72 general practices with a combined list size of 480,942 patients were randomised. At 6 months' follow-up, patients in the PINCER group were significantly less likely to have been prescribed a non-selective NSAID if they had a history of peptic ulcer without gastroprotection (OR 0·58, 95% CI 0·38-0·89); a β blocker if they had asthma (0·73, 0·58-0·91); or an ACE inhibitor or loop diuretic without appropriate monitoring (0·51, 0·34-0·78). PINCER has a 95% probability of being cost effective if the decision-maker's ceiling willingness to pay reaches £75 per error avoided at 6 months.
Interpretation: The PINCER intervention is an effective method for reducing a range of medication errors in general practices with computerised clinical records.
Funding: Patient Safety Research Portfolio, Department of Health, England.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Improving medication safety.Lancet. 2012 Apr 7;379(9823):1278-80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60078-6. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22357107 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gandhi TK, Weingart SN, Borus J. Adverse drug events in ambulatory care. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1556–1564. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Field TS, Harrold LR. Incidence and preventability of adverse drug events among older persons in the ambulatory setting. JAMA. 2003;289:1107–1116. - PubMed
-
- Bates DW, Cullen DJ, Laird N. Incidence of adverse drug events and potential adverse drug events: implications for prevention. JAMA. 1995;274:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health . An organisation with a memory: report of an expert group on learning from adverse events in the NHS. Department of Health; London: 2000.
-
- Kohn L, Corrigan J, Donaldson M. To err is human—building a safer health system. Institute of Medicine; Washington, DC: 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

