Polysaccharides from astragali radix restore chemical-induced blood vessel loss in zebrafish
- PMID: 22357377
- PMCID: PMC3316134
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-824X-4-2
Polysaccharides from astragali radix restore chemical-induced blood vessel loss in zebrafish
Abstract
Background: Astragali Radix has been used widely for the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, and to enhance endurance and stamina in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for over 2000 years. The polysaccharide constituents of Astragali Radix (ARP) are considered as one of the major constituents contributing to the multiple pharmacological effects of this medicinal plant. The purpose of the study is to evaluate the vascular regenerative activities of ARPs in a chemically-induced blood vessel loss model in zebrafish.
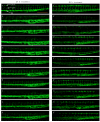
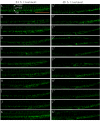
Methods: Blood vessel loss was induced in both Tg(fli-1a:EGFP)y1 and Tg(fli-1a:nEGFP)y7 embryos by administration of 300 nM VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor II (VRI) for 3 h at 24 hpf (hour post-fertilization). Then, the blood vessel damaged zebrafish were treated with ARPs for 21 h and 45 h after VRI withdrawal. Morphological changes in intersegmental vessels (ISVs) of zebrafish larvae were observed under the fluorescence microscope and measured quantitatively. The rescue effect of ARPs in the zebrafish models was validated by measuring the relative mRNA expressions of Kdrl, Kdr and Flt-1 using real-time PCR.
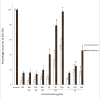
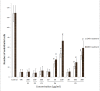
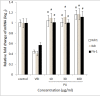
Results: Two polysaccharide fractions, P4 (50000 D < molecular weight & diameter < 0.1 μm) and P5 (molecular diameter > 0.1 μm), isolated from Astragali Radix by ultrafiltration, produced a significant and dose-dependent recovery in VRI-induced blood vessel loss in zebrafish. Furthermore, the down-regulation of Flk-1 and Flt-1 mRNA expression induced by VRI was reversed by treatment with P4.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrates that P4 isolated from Astragali Radix reduces VRI-induced blood vessel loss in zebrafish. These findings support the hypothesis that polysaccharides are one of the active constituents in Astragali Radix, contributing to its beneficial effect on treatment of diseases associated with a deficiency in angiogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatholobi Caulis extracts promote angiogenesis in HUVECs in vitro and in zebrafish embryos in vivo via up-regulation of VEGFRs.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.075. Epub 2016 Oct 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27989880
-
Anti-thrombotic and pro-angiogenic effects of Rubia cordifolia extract in zebrafish.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jun 12;219:152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29126989
-
Paeoniflorin Promotes Angiogenesis in A Vascular Insufficiency Model of Zebrafish in vivo and in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells in vitro.Chin J Integr Med. 2018 Jul;24(7):494-501. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2262-2. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 27286711
-
Biological active ingredients of Astragali Radix and its mechanisms in treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.Phytomedicine. 2022 Apr;98:153918. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153918. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35104756 Review.
-
Danggui Buxue Tang (Astragali Radix and Angelicae Sinensis Radix) for menopausal symptoms: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 6;199:205-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.044. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28163116 Review.
Cited by
-
Compatibility Study of Danggui Buxue Tang on Chemical Ingredients, Angiogenesis and Endothelial Function.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 22;7:45111. doi: 10.1038/srep45111. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28327640 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical Exploring of a Molecular Mechanism for Melanin Inhibitory Activity of Calycosin in Zebrafish.Molecules. 2021 Nov 19;26(22):6998. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226998. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834088 Free PMC article.
-
From omics to drug metabolism and high content screen of natural product in zebrafish: a new model for discovery of neuroactive compound.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:605303. doi: 10.1155/2012/605303. Epub 2012 Aug 5. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22919414 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Developmental Toxicity Induced by E804 in Zebrafish Embryos.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 14;11:32. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00032. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32116709 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Pharmaceutical Properties and Value of Astragali Radix.Medicines (Basel). 2018 May 21;5(2):46. doi: 10.3390/medicines5020046. Medicines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29883402 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodriguez-Martinez S, Cancino-Diaz ME, Miguel PS, Cancino-Diaz JC. Lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor via toll-like receptor 4 in human limbal fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2006;83:1373–1377. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.07.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Croci DO, Cumashi A, Ushakova NA, Preobrazhenskaya ME, Piccoli A, Totani L, Ustyuzhanina NE, Bilan MI, Usov AI, Grachev AA, Morozevich GE, Berman AE, Sanderson CJ, Kelly M, Di Gregorio P, Rossi C, Tinari N, Iacobelli S, Rabinovich GA, Nifantiev NE. Fucans, but not fucomannoglucuronans, determine the biological activities of sulfated polysaccharides from Laminaria saccharina brown seaweed. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017283. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

