Minocycline and aspirin in the treatment of bipolar depression: a protocol for a proof-of-concept, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2x2 clinical trial
- PMID: 22357572
- PMCID: PMC3289990
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000643
Minocycline and aspirin in the treatment of bipolar depression: a protocol for a proof-of-concept, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2x2 clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: New medication classes are needed to improve treatment effectiveness in the depressed phase of bipolar disorder (BD). Extant evidence suggests that BD is characterised by neural changes such as dendritic remodelling and glial and neuronal cell loss. These changes have been hypothesised to result from chronic inflammation. The principal aims of the proposed research is to evaluate the antidepressant efficacy in bipolar depression of minocycline, a drug with neuroprotective and immune-modulating properties, and of aspirin, at doses expected to selectively inhibit cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1).
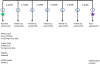
Methods and analysis: 120 outpatients between 18 and 55 years of age, who meet DSM-IV-TR criteria for BD (type I or II) and for a current major depressive episode will be recruited to take part in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, proof-of-concept clinical trial following a 2×2 design. As adjuncts to existing treatment, subjects will be randomised to receive one of the four treatment combinations: placebo-minocycline plus placebo-aspirin, active-minocycline plus placebo-aspirin, placebo-minocycline plus active-aspirin or active-minocycline plus active-aspirin. The dose of minocycline and aspirin is 100 mg twice daily and 81 mg twice daily, respectively. Antidepressant response will be evaluated by assessing changes in the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale scores between baseline and the end of the 6-week trial. As secondary outcome measures, the anti-inflammatory effects of minocycline and aspirin will be tested by measuring pre-treatment and post-treatment levels of C reactive protein and inflammatory cytokines.
Ethics and dissemination: Minocycline has been widely used as an antibiotic in doses up to 400 mg/day. Low-dose aspirin has been safely used on a worldwide scale for its role as an antithrombotic and thrombolytic. The study progress will be overseen by a Data, Safety and Monitoring Board, which will meet once every 6 months. Results of the study will be published in peer-reviewed publications.
Trial registration number: Clinical Trials.gov: NCT01429272.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of bipolar depression with minocycline and/or aspirin: an adaptive, 2×2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase IIA clinical trial.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Jan 24;8(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41398-017-0073-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29362444 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of inflammation-based stratification for add-on celecoxib or minocycline in major depressive disorder: Protocol of the INSTA-MD double-blind placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Sep 19;41:100871. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100871. eCollection 2024 Nov. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39350954 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline and celecoxib as adjunctive treatments for bipolar depression: a multicentre, factorial design randomised controlled trial.Lancet Psychiatry. 2020 Jun;7(6):515-527. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30138-3. Epub 2020 May 20. Lancet Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32445690 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
-
Protocol and rationale-the efficacy of minocycline as an adjunctive treatment for major depressive disorder: a double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2014 Dec;12(3):180-8. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2014.12.3.180. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25598820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Population scale retrospective analysis reveals distinctive antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of diclofenac, ketoprofen and naproxen in patients with pain.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 18;13(4):e0195521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195521. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29668764 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the immune system in the treatment of bipolar disorder.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Oct;236(10):2909-2921. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-5175-x. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30756134 Review.
-
Bipolar Disorder: Role of Inflammation and the Development of Disease Biomarkers.Psychiatry Investig. 2016 Jan;13(1):18-33. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.1.18. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Psychiatry Investig. 2016. PMID: 26766943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Aspirin Treatment on Neurotransmitters' Tissue Content in Rats' Hippocampus and Amygdala.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 4;13(4):515. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040515. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110173 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation as a Mechanism of Bipolar Disorder Neuroprogression.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2021;48:215-237. doi: 10.1007/7854_2020_173. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33040314
References
-
- Correa R, Akiskal H, Gilmer W, et al. Is unrecognized bipolar disorder a frequent contributor to apparent treatment resistant depression? J Affect Disord 2010;127:10–18 - PubMed
-
- Tohen M, Vieta E, Calabrese J, et al. Efficacy of olanzapine and olanzapine-fluoxetine combination in the treatment of bipolar I depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003;60:1079–88 - PubMed
-
- Nierenberg AA, Ostacher MJ, Calabrese JR, et al. Treatment-resistant bipolar depression: a STEP-BD equipoise randomized effectiveness trial of antidepressant augmentation with lamotrigine, inositol, or risperidone. Am J Psychiatry 2006;163:210–16 - PubMed
-
- Nemeroff CB, Evans DL, Gyulai L, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of imipramine and paroxetine in the treatment of bipolar depression. Am J Psychiatry 2001;158:906–12 - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
