Requirement of translocated lysosomal V1 H(+)-ATPase for activation of membrane acid sphingomyelinase and raft clustering in coronary endothelial cells
- PMID: 22357614
- PMCID: PMC3327313
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-09-0821
Requirement of translocated lysosomal V1 H(+)-ATPase for activation of membrane acid sphingomyelinase and raft clustering in coronary endothelial cells
Abstract
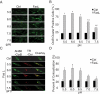
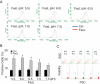
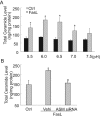
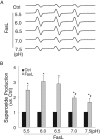
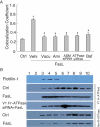
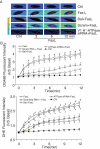
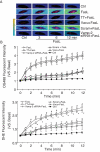
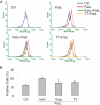
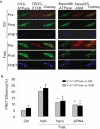
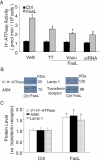
Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) mediates the formation of membrane raft (MR) redox signalosomes in a process that depends on a local acid microenvironment in coronary arterial endothelial cells (CAECs). However, it is not known how this local acid microenvironment is formed and maintained. The present study hypothesized that lysosomal V1 H(+)-ATPase provides a hospitable acid microenvironment for activation of ASM when lysosomes traffic and fuse into the cell membrane. Confocal microscopy showed that local pH change significantly affected MRs, with more fluorescent patches under low pH. Correspondingly, the ASM product, ceramide, increased locally in the cell membrane. Electron spin resonance assay showed that local pH increase significantly inhibited NADPH oxidase-mediated production of O(2)(-.) in CAECs. Direct confocal microscopy demonstrated that Fas ligand resulted in localized areas of decreased pH around CAEC membranes. The inhibitors of both lysosomal fusion and H(+)-ATPase apparently attenuated FasL-caused pH decrease. V1 H(+)-ATPase accumulation and activity on cell membranes were substantially suppressed by the inhibitors of lysosomal fusion or H(+)-ATPase. These results provide the first direct evidence that translocated lysosomal V1 H(+)-ATPase critically contributes to the formation of local acid microenvironment to facilitate activation of ASM and consequent MR aggregation, forming MR redox signalosomes and mediating redox signaling in CAECs.
Figures
References
-
- Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:128–140. - PubMed
-
- Baader AP, Buchler L, Bircher-Lehmann L, Kleber AG. Real time, confocal imaging of Ca(2+) waves in arterially perfused rat hearts. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;53:105–115. - PubMed
-
- Belusa R, Wang ZM, Matsubara T, Sahlgren B, Dulubova I, Nairn AC, Ruoslahti E, Greengard P, Aperia A. Mutation of the protein kinase C phosphorylation site on rat alpha1 Na+,K+-ATPase alters regulation of intracellular Na+ and pH and influences cell shape and adhesiveness. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:20179–20184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

