Neurabin scaffolding of adenosine receptor and RGS4 regulates anti-seizure effect of endogenous adenosine
- PMID: 22357852
- PMCID: PMC3310383
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4125-11.2011
Neurabin scaffolding of adenosine receptor and RGS4 regulates anti-seizure effect of endogenous adenosine
Abstract
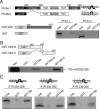
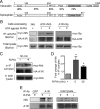
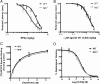
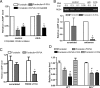
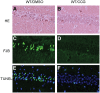
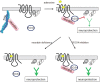
Endogenous adenosine is an essential protective agent against neural damage by various insults to the brain. However, the therapeutic potential of adenosine receptor-directed ligands for neuroprotection is offset by side effects in peripheral tissues and organs. An increase in adenosine receptor responsiveness to endogenous adenosine would enhance neuroprotection while avoiding the confounding effects of exogenous ligands. Here we report novel regulation of adenosine-evoked responses by a neural tissue-specific protein, neurabin. Neurabin attenuated adenosine A(1) receptor (A1R) signaling by assembling a complex between the A1R and the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4), a protein known to turn off G-protein signaling. Inactivation of the neurabin gene enhanced A1R signaling and promoted the protective effect of adenosine against excitotoxic seizure and neuronal death in mice. Furthermore, administration of a small molecule inhibitor of RGS4 significantly attenuated seizure severity in mice. Notably, the dose of kainate capable of inducing an ∼50% rate of death in wild-type (WT) mice did not affect neurabin-null mice or WT mice cotreated with an RGS4 inhibitor. The enhanced anti-seizure and neuroprotective effect achieved by disruption of the A1R/neurabin/RGS4 complex is elicited by the on-site and on-demand release of endogenous adenosine, and does not require administration of A1R ligands. These data identify neurabin-RGS4 as a novel tissue-selective regulatory mechanism for fine-tuning adenosine receptor function in the nervous system. Moreover, these findings implicate the A1R/neurabin/RGS4 complex as a valid therapeutic target for specifically manipulating the neuroprotective effects of endogenous adenosine.
Figures



Comment in
-
Neurabin: a key factor in the specific neuroprotection mediated by Adenosine.Purinergic Signal. 2012 Dec;8(4):659-60. doi: 10.1007/s11302-012-9333-4. Purinergic Signal. 2012. PMID: 22992978 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effective Attenuation of Adenosine A1R Signaling by Neurabin Requires Oligomerization of Neurabin.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;92(6):630-639. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.109462. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28954816 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide blocking the ADORA1-neurabin interaction is anticonvulsant and inhibits epilepsy in an Alzheimer's model.JCI Insight. 2022 Jun 8;7(11):e155002. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.155002. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35674133 Free PMC article.
-
Regulator of G Protein Signalling 4 (RGS4) as a Novel Target for the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 22;22(1):3. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010003. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374915 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A1 receptors are crucial in keeping an epileptic focus localized.Exp Neurol. 2006 Jul;200(1):184-90. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.02.133. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16750195
-
Adenosine A1 receptor activation modulates N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) preconditioning phenotype in the brain.Behav Brain Res. 2015 Apr 1;282:103-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.12.056. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25557798
Cited by
-
Regulation of Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity by Protein Phosphatase 1.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;41(14):3040-3050. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2026-20.2021. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33827970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The amyloid precursor protein modulates α2A-adrenergic receptor endocytosis and signaling through disrupting arrestin 3 recruitment.FASEB J. 2017 Oct;31(10):4434-4446. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700346R. Epub 2017 Jun 23. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28646018 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic regulation of Rgs4 mRNA by HuR and miR-26/RISC in neurons.RNA Biol. 2021 Jul;18(7):988-998. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1795409. Epub 2020 Aug 11. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32779957 Free PMC article.
-
A scaffold as a platform for new therapies?Epilepsy Curr. 2012 Sep;12(5):172-3. doi: 10.5698/1535-7511-12.5.172. Epilepsy Curr. 2012. PMID: 23118599 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interplay of cysteine exposure and global protein dynamics in small-molecule recognition by a regulator of G-protein signaling protein.Proteins. 2019 Feb;87(2):146-156. doi: 10.1002/prot.25642. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Proteins. 2019. PMID: 30521141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen PB, Zachariou V, Svenningsson P, Lepore AC, Centonze D, Costa C, Rossi S, Bender G, Chen G, Feng J, Snyder GL, Bernardi G, Nestler EJ, Yan Z, Calabresi P, Greengard P. Distinct roles for spinophilin and neurabin in dopamine-mediated plasticity. Neuroscience. 2006;140:897–911. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Wilkie TM, Gilman AG. GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the Gi subfamily of G protein alpha subunits. Cell. 1996;86:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Berman RF, Fredholm BB, Aden U, O'Connor WT. Evidence for increased dorsal hippocampal adenosine release and metabolism during pharmacologically induced seizures in rats. Brain Res. 2000;872:44–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
