Na delivery and ENaC mediate flow regulation of collecting duct endothelin-1 production
- PMID: 22357920
- PMCID: PMC3362067
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00034.2012
Na delivery and ENaC mediate flow regulation of collecting duct endothelin-1 production
Abstract
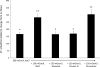
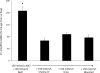
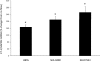
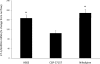
Collecting duct (CD) endothelin-1 (ET-1) is an important autocrine inhibitor of Na and water transport. CD ET-1 production is stimulated by extracellular fluid volume expansion and tubule fluid flow, suggesting a mechanism coupling CD Na delivery and ET-1 synthesis. A mouse cortical CD cell line, mpkCCDc14, was subjected to static or flow conditions for 2 h at 2 dyn/cm(2), followed by determination of ET-1 mRNA content. Flow with 300 mosmol/l NaCl increased ET-1 mRNA to 65% above that observed under static conditions. Increasing perfusate osmolarity to 450 mosmol/l with NaCl or Na acetate increased ET-1 mRNA to ∼184% compared with no flow, which was not observed when osmolarity was increased using mannitol or urea. Reducing Na concentration to 150 mosmol/l while maintaining total osmolarity at 300 mosmol/l with urea or mannitol decreased the flow response. Inhibition of epithelial Na channel (ENaC) with amiloride or benzamil abolished the flow response, suggesting involvement of ENaC in flow-regulated ET-1 synthesis. Aldosterone almost doubled the flow response. Since Ca(2+) enhances CD ET-1 production, the involvement of plasma membrane and mitochondrial Na/Ca(2+) exchangers (NCX) was assessed. SEA0400 and KB-R7943, plasma membrane NCX inhibitors, did not affect the flow response. However, CGP37157, a mitochondrial NCX inhibitor, abolished the response. In summary, the current study indicates that increased Na delivery, leading to ENaC-mediated Na entry and mitochondrial NCX activity, is involved in flow-stimulated CD ET-1 synthesis. This constitutes the first report of either ENaC or mitochondrial NCX regulation of an autocrine factor in any biologic system.
Figures
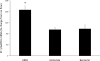
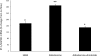
References
-
- Belmonte S, Morad M. Shear fluid-induced Ca2+ release and the role of mitochondria in rat cardiac myocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1123: 58–63, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Birinyi P, Acsai K, Banyasz T, Toth A, Horvath B, Virag L, Szentandrassy N, Magyar J, Varro A, Fulop F, Nanasi PP. Effects of SEA0400 and KB-R7943 on Na+/Ca2+ exchange current and L-type Ca2+ current in canine ventricular cardiomyocytes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 372: 63–70, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chu T, Wu MS, Hsieh BS. Urinary endothelin-1 in patients with renal disease. J Formos Med Assoc 97: 667–672, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

