Molecular links between mitochondrial dysfunctions and schizophrenia
- PMID: 22358509
- PMCID: PMC3887718
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-012-2284-3
Molecular links between mitochondrial dysfunctions and schizophrenia
Abstract
Schizophrenia is a complex neuropsychiatric disorder with both neurochemical and neurodevelopmental components in the pathogenesis. Growing pieces of evidence indicate that schizophrenia has pathological components that can be attributable to the abnormalities of mitochondrial function, which is supported by the recent finding suggesting mitochondrial roles for Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1). In this minireview, we briefly summarize the current understanding of the molecular links between mitochondrial dysfunctions and the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, covering recent findings from human genetics, functional genomics, proteomics, and molecular and cell biological approaches.
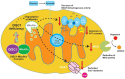
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) plays essential roles in mitochondria in collaboration with Mitofilin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 12;107(41):17785-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004361107. Epub 2010 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20880836 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted in schizophrenia 1 (DISC1): subcellular targeting and induction of ring mitochondria.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Dec;30(4):477-84. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.08.021. Epub 2005 Oct 4. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16209927
-
Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) is a multicompartmentalized protein that predominantly localizes to mitochondria.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004 May;26(1):112-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.01.013. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15121183
-
Molecular mechanism of schizophrenia with reference to disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1).Neurochem Int. 2007 Jul-Sep;51(2-4):165-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.06.018. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Neurochem Int. 2007. PMID: 17664024 Review.
-
Role of DISC1 in neural development and schizophrenia.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Feb;17(1):95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17258902 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical Properties and Physiological Functions of pLG72: Twenty Years of Investigations.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 20;12(6):858. doi: 10.3390/biom12060858. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Changes in High-Energy Compounds in Different Cellular Models Associated to Hypoxia: Implication to Schizophrenia.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 2;9(1):18049. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53605-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31792231 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia: a disorder of broken brain bioenergetics.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 May;27(5):2393-2404. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01494-x. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35264726 Review.
-
Dynamic Changes of the Mitochondria in Psychiatric Illnesses: New Mechanistic Insights From Human Neuronal Models.Biol Psychiatry. 2018 May 1;83(9):751-760. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29486891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Serotonin and Dopamine Activity Modulators in the Treatment of Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Rapid Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 16;11(3):921. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030921. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akyol O., Yanik M., Elyas H., Namli M., Canatan H., Akin H., Yuce H., Yilmaz H.R., Tutkun H., Sogut S., et al. Association between Ala-9Val polymorphism of Mn-SOD gene and schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005;29:123–131. - PubMed
-
- Altar C.A., Jurata L.W., Charles V., Lemire A., Liu P., Bukhman Y., Young T.A., Bullard J., Yokoe H., Webster M.J., et al. Deficient hippocampal neuron expression of proteasome, ubiquitin, and mitochondrial genes in multiple schizophrenia cohorts. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005;58:85–96. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic criteria from DSM-IV-TR. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

