Structural basis of highly conserved ribosome recycling in eukaryotes and archaea
- PMID: 22358840
- PMCID: PMC6878762
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10829
Structural basis of highly conserved ribosome recycling in eukaryotes and archaea
Abstract
Ribosome-driven protein biosynthesis is comprised of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. In bacteria, ribosome recycling requires ribosome recycling factor and elongation factor G, and several structures of bacterial recycling complexes have been determined. In the eukaryotic and archaeal kingdoms, however, recycling involves the ABC-type ATPase ABCE1 and little is known about its structural basis. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions of eukaryotic and archaeal ribosome recycling complexes containing ABCE1 and the termination factor paralogue Pelota. These structures reveal the overall binding mode of ABCE1 to be similar to canonical translation factors. Moreover, the iron-sulphur cluster domain of ABCE1 interacts with and stabilizes Pelota in a conformation that reaches towards the peptidyl transferase centre, thus explaining how ABCE1 may stimulate peptide-release activity of canonical termination factors. Using the mechanochemical properties of ABCE1, a conserved mechanism in archaea and eukaryotes is suggested that couples translation termination to recycling, and eventually to re-initiation.
Figures
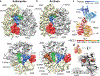




References
-
- Winzeler EA et al. Functional characterization of the S. cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285, 901–906 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Coelho CM et al. Growth and cell survival are unevenly impaired in pixie mutant wing discs. Development 132, 5411–5424 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Estevez AM, Haile S, Steinbuchel M, Quijada L & Clayton C. Effects of depletion and overexpression of the Trypanosoma brucei ribonuclease L inhibitor homologue. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 133, 137–141 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

