Epidermal growth factor receptor and K-Ras mutations and resistance of lung cancer to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 22359227
- PMCID: PMC3674414
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.26656
Epidermal growth factor receptor and K-Ras mutations and resistance of lung cancer to insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Erratum in
- Cancer. 2012 Dec 15;118(24):6301
Abstract
Background: Most patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have responded poorly to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The authors investigated the involvement of insulinlike growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) signaling in primary resistance to EGFR TKIs and the molecular determinants of resistance to IGF-1R TKIs.
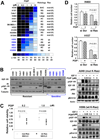
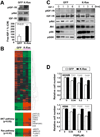
Methods: Phosphorylated IGF-1R/insulin receptor (pIGF-1R/IR) was immunohistochemically evaluated in an NSCLC tissue microarray. The authors analyzed the antitumor effects of an IGF-1R TKI (PQIP or OSI-906), either alone or in combination with a small-molecular inhibitor (PD98059 or U0126) or with siRNA targeting K-Ras or mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK), in vitro and in vivo in NSCLC cells with variable histologic features and EGFR or K-Ras mutations.
Results: pIGF-1R/IR expression in NSCLC specimens was associated with a history of tobacco smoking, squamous cell carcinoma histology, mutant K-Ras, and wild-type (WT) EGFR, all of which have been strongly associated with poor response to EGFR TKIs. IGF-1R TKIs exhibited significant antitumor activity in NSCLC cells with WT EGFR and WT K-Ras but not in those with mutations in these genes. Introduction of mutant K-Ras attenuated the effects of IGF-1R TKIs on NSCLC cells expressing WT K-Ras. Conversely, inactivation of MEK restored sensitivity to IGF-TKIs in cells carrying mutant K-Ras.
Conclusions: The mutation status of both EGFR and K-Ras could be a predictive marker of response to IGF-1R TKIs. Also, MEK antagonism can abrogate primary resistance of NSCLC cells to IGF-1R TKIs.
Copyright © 2012 American Cancer Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) predicts poor responses to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring activating EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2015 Mar;87(3):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25617986
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) as a biomarker for resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2013 Jul;36(4):277-88. doi: 10.1007/s13402-013-0133-9. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 23619944 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced expression of EI24 confers resistance to gefitinib through IGF-1R signaling in PC9 NSCLC cells.Lung Cancer. 2015 Nov;90(2):175-81. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.08.019. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26342551
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a 4-aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-based dual IGF1R/Src inhibitor as a novel anticancer agent with minimal toxicity.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0802-4. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455661 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Receptor Activation in Lung Cancer.Malays J Med Sci. 2016 May;23(3):9-21. Malays J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27418865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compounds from the marine sponge Cribrochalina vasculum offer a way to target IGF-1R mediated signaling in tumor cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50258-50276. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10361. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384680 Free PMC article.
-
miR-145 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of Y79 human retinoblastoma cells by targeting IGF-1R.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Sep 1;11(9):4331-4338. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949829 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic implications of tumoral expression of insulin like growth factors 1 and 2 in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2014 May;15(3):213-21. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2013.12.006. Epub 2014 Jan 1. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24485233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57(1):43–66. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304(5676):1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(2):123–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

