A strong deletion bias in nonallelic gene conversion
- PMID: 22359514
- PMCID: PMC3280953
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002508
A strong deletion bias in nonallelic gene conversion
Abstract
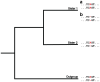
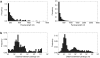
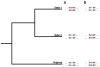
Gene conversion is the unidirectional transfer of genetic information between orthologous (allelic) or paralogous (nonallelic) genomic segments. Though a number of studies have examined nucleotide replacements, little is known about length difference mutations produced by gene conversion. Here, we investigate insertions and deletions produced by nonallelic gene conversion in 338 Drosophila and 10,149 primate paralogs. Using a direct phylogenetic approach, we identify 179 insertions and 614 deletions in Drosophila paralogs, and 132 insertions and 455 deletions in primate paralogs. Thus, nonallelic gene conversion is strongly deletion-biased in both lineages, with almost 3.5 times as many conversion-induced deletions as insertions. In primates, the deletion bias is considerably stronger for long indels and, in both lineages, the per-site rate of gene conversion is orders of magnitudes higher than that of ordinary mutation. Due to this high rate, deletion-biased nonallelic gene conversion plays a key role in genome size evolution, leading to the cooperative shrinkage and eventual disappearance of selectively neutral paralogs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Koonin EV. Orthologs, paralogs, and evolutionary genomics. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;39:309–338. - PubMed
-
- Gojobori T, Li WH, Graur D. Patterns of nucleotide substitution in pseudogenes and functional genes. J Mol Evol. 1982;18:360–369. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Valin F, Lamollea G, Bernardi G. Isochores, GC3 and mutation biases in the human genome. Gene. 2002;300:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Petrov DA. Mutational Equilibrium Model of Genome Size Evolution. Theor Popul Biol. 2002;61:531–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

