Repression of a potassium channel by nuclear hormone receptor and TGF-β signaling modulates insulin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 22359515
- PMCID: PMC3280960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002519
Repression of a potassium channel by nuclear hormone receptor and TGF-β signaling modulates insulin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
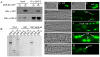
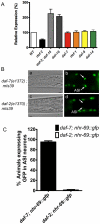
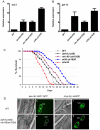
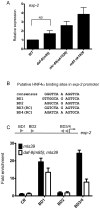
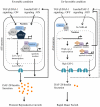
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling acts through Smad proteins to play fundamental roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and metabolism. The Receptor associated Smads (R-Smads) interact with DNA and other nuclear proteins to regulate target gene transcription. Here, we demonstrate that the Caenorhabditis elegans R-Smad DAF-8 partners with the nuclear hormone receptor NHR-69, a C. elegans ortholog of mammalian hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α HNF4α), to repress the exp-2 potassium channel gene and increase insulin secretion. We find that NHR-69 associates with DAF-8 both in vivo and in vitro. Functionally, daf-8 nhr-69 double mutants show defects in neuropeptide secretion and phenotypes consistent with reduced insulin signaling such as increased expression of the sod-3 and gst-10 genes and a longer life span. Expression of the exp-2 gene, encoding a voltage-gated potassium channel, is synergistically increased in daf-8 nhr-69 mutants compared to single mutants and wild-type worms. In turn, exp-2 acts selectively in the ASI neurons to repress the secretion of the insulin-like peptide DAF-28. Importantly, exp-2 mutation shortens the long life span of daf-8 nhr-69 double mutants, demonstrating that exp-2 is required downstream of DAF-8 and NHR-69. Finally, animals over-expressing NHR-69 specifically in DAF-28-secreting ASI neurons exhibit a lethargic, hypoglycemic phenotype that is rescued by exogenous glucose. We propose a model whereby DAF-8/R-Smad and NHR-69 negatively regulate the transcription of exp-2 to promote neuronal DAF-28 secretion, thus demonstrating a physiological crosstalk between TGF-β and HNF4α-like signaling in C. elegans. NHR-69 and DAF-8 dependent regulation of exp-2 and DAF-28 also provides a novel molecular mechanism that contributes to the previously recognized link between insulin and TGF-β signaling in C. elegans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
dbl-1/TGF-β and daf-12/NHR Signaling Mediate Cell-Nonautonomous Effects of daf-16/FOXO on Starvation-Induced Developmental Arrest.PLoS Genet. 2015 Dec 11;11(12):e1005731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005731. eCollection 2015 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26656736 Free PMC article.
-
The DAF-7/TGF-β signaling pathway regulates abundance of the Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate receptor GLR-1.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26054666 Free PMC article.
-
PDP-1 links the TGF-β and IIS pathways to regulate longevity, development, and metabolism.PLoS Genet. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1001377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001377. Epub 2011 Apr 21. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21533078 Free PMC article.
-
The 'nuclear option' revisited: Confirmation of Ss-daf-12 function and therapeutic potential in Strongyloides stercoralis and other parasitic nematode infections.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022 Jul;250:111490. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2022.111490. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35697206 Review.
-
Hormesis and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Exp Gerontol. 2006 Oct;41(10):935-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Oct 24. Exp Gerontol. 2006. PMID: 17067771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear hormone receptor NHR-49 is an essential regulator of stress resilience and healthy aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Physiol. 2023 Aug 14;14:1241591. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1241591. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37645565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β signaling in C. elegans.WormBook. 2013 Jul 10:1-34. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.22.2. WormBook. 2013. PMID: 23908056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional and spatiotemporal regulation of the dauer program.Transcription. 2023 Nov;14(1-2):27-48. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2023.2190295. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Transcription. 2023. PMID: 36951297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic effect of testosterone in the behavior of C. elegans. A clue to explain androgen-dependent autistic traits?Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Mar 4;8:69. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00069. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24624060 Free PMC article.
-
Gain-of-Function Alleles in Caenorhabditis elegans Nuclear Hormone Receptor nhr-49 Are Functionally Distinct.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 12;11(9):e0162708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162708. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27618178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massagué J, Gomis R. The logic of TGFbeta signaling. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:2811–20. - PubMed
-
- Attisano L, Carcamo J, Ventura F, Weis F. Identification of Human Activin and TGF Type I Receptors That Form Heteromeric Kinase Complexes. CELL-CAMBRIDGE MA- 1993;75:671–680. - PubMed
-
- Riddle DL, Swanson MM, Albert PS. Interacting genes in nematode dauer larva formation. Nature. 1981;290:668–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

